| This document is very much a work in progress. |
1. Intro
c-xrefactory is a software tool and a project aiming at restoring the sources of that
old, but very useful, tool to a state where it can be enhanced and be the foundation for
a highly capable refactoring browser.
It is currently in excellent working condition, so you can use it in your daily work. I do. For information about how to do that, see the README.md.
1.1. Caution
As indicated by the README.md, this is a long term restoration project. So anything you find in this document might be old, incorrect, guesses, temporary holders for thoughts or theories. Or actually true and useful.
Especially names of variables, functions and modules is prone to change as understanding of them increases. They might also be refactored into something entirently different.
This document has progressed from non-existing, to a collection of unstructured thougths, guesses, historic anecdotes, ideas and a collection of unstructured, pre-existing, wiki pages, and is now quite useful. Perhaps it will continue to be improved and "refactored" into something valuable for anyone who venture into this project.
The last part of this document is an Archive where completely obsolete descriptions have been moved for future software archeologists to find.
1.2. Background
You will find some background about the project in the README.md.
This document tries to collect the knowledge and understanding about how c-xrefactory
actually works, plans for making it better, both in terms of working with the source,
its structure and its features.
Hopefully over time this will be the design documentation of c-xrefactory, which, at
that time, will be a fairly well structured and useful piece of software.
1.3. Goal
Ultimately c-xrefactory could become the refactoring browser for C, the one that
everybody uses. As suggested by @tajmone in GitHub issue #39, by switching to a general
protocol, we could possibly plug this in to many editors.
However, to do that we need to refactor out the protocol parts. And to do that we need a better structure, and to dare to change that, we need to understand more of the intricacies of this beast, and we need tests. So the normal legacy code catch 22 applies…
Test coverage is starting to look good, coming up to slightly above 80% at the time of writing this. Many "tests" are just "application level" execution, rather than actual tests, but also this is improving.
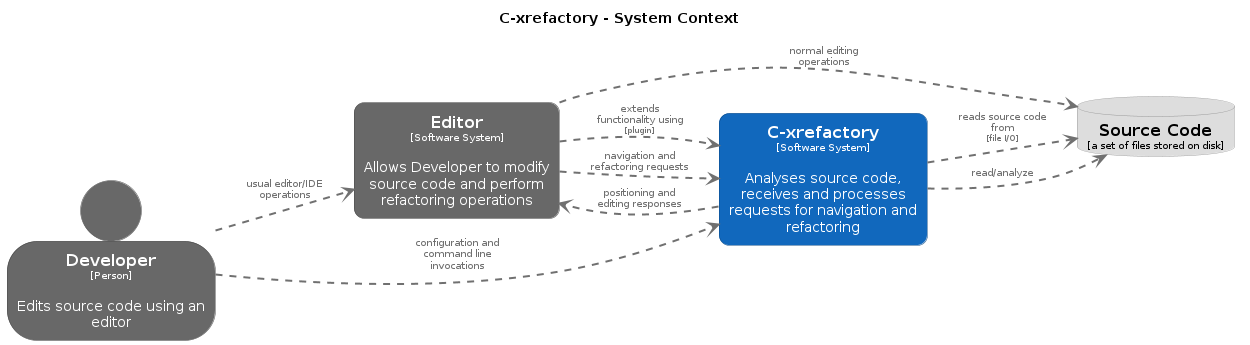
2. Context
c-xrefactory is designed to be an aid for programmers as they write,
edit, inspect, read and improve the code they are working on.
The editor is used for usual manual manipulation of the source
code. C-xrefactory interacts with the editor to provide navigation
and automated edits, refactorings, through the editor.
3. Functional Overview
The c-xref program is, or rather was, a mish-mash of a multitude of features baked into one program. This is the major cause of the mess that it is source-wise.
It was
-
a generator for persistent cross-reference data
-
a reference server for editors, serving cross-reference, navigational and completion data over a protocol
-
a refactoring server (the worlds first to cross the Refactoring Rubicon)
-
an HTML cross-reference generator (probably the root of the project) (REMOVED)
-
a C macro generator for structure fill (and other) functions (REMOVED)
It is the first three that are unique and constitutes the great value of this project. The last two have been removed from the source, the last one because it was a hack and prevented modern, tidy, building, coding and refactoring. The HTML cross-reference generator has been superseeded by modern alternatives like Doxygen and is not at the core of the goal of this project.
One might surmise that it was the HTML-crossreference generator that
was the initial purpose of what the original Xrefactory was based
upon. Once that was in place the other followed, and were basically
only bolted on top without much re-architecting the C sources.
What we’d like to do is partition the project into separate parts, each having a clear usage.
The following sections are aimed at describing various features of
c-xrefactory.
3.1. Main functionality
A programmer constantly needs to navigate, understand and improve the source code in order to lessen the cognitive load for understanding and making changes.
c-xrefactory provides two sets of functions for this directly from
within the editor
-
navigation, searching and browsing symbols
-
automated refactorings, i.e. non-behaviour changing edits
C and Yacc source code is supported.
3.1.1. Navigation
A user can navigate all references of a symbol, limited to the semantic scope of that symbol, by "Goto Definition" and then navigate using "Next/previous Reference". This is a fast way to inspect where a symbol is used.
| This also applies to non-terminals and semantic attributes in Yacc grammars! |
3.1.2. Searching
A user can search for symbols by name using two operations:
- Search Symbol
-
Finds all symbols whose name matches the search pattern. This includes functions, variables, types, macros — any symbol known to
c-xrefactory, whether or not it is defined in the project. - Search Definition
-
Finds only symbols that have a definition within the project. Symbols that are merely used (e.g. called from an external library) are excluded.
Both operations accept wildcard patterns: matches any sequence of
characters and ? matches a single character. For example, parse
finds all symbols starting with "parse", while get_? finds
three-letter symbols starting with "get_".
The search results are presented in a list. Use the up/down arrow keys to move between entries. Press RET to inspect a symbol — this navigates to its definition and enters the reference browser where Next/Previous Reference can be used to visit all references.
Pressing p and n in the search results navigates the search
history — returning to the results of a previous or next search, not
moving between entries in the current list.
| Search currently reads from the on-disk references database, not from the live in-memory state. The database is saved automatically when Emacs exits or when the server is restarted. If the database has never been saved, search will return no results. |
3.1.3. Completion
As c-xrefactory have information about symbols and their semantic scope,
it can also provide semantically informed completions and suggestions.
3.1.4. Automated refactorings
In his book "Refactoring" Martin Fowler describes a large number of refactorings, changes to source code that does not change the behaviour, but improves it structure and readability. For each refactoring they describe step by step which edits to make to apply the refactoring manually.
The natural next step was of course to attempt to automate this in editors or IDEs, which started to happen.
In an article from 2001 Martin pronounces Xref, the ancestor to c-xrefactory, to be
the first tool to cross "Refactorings Rubicon", being able to extract a function
semantically correct.
The term "automated" means that some software can examine the source
code and quickly and safely modify it using patterns from the list of
possible refactorings, without user interaction. Many refactorings in
the book, and on the website, are applicable mostly for OO-languages,
but many also apply to C. c-xrefactory can perform some of
them. More are considered for implementation.
-
"Rename Symbol" - change the name of a variable, type, function only for the semantic scope of the symbol
-
"Extract Macro/Function" - a region of the code can be extracted to a new function or macro
-
"Organize Includes" - clean up a list of #include directives by particioning and sorting them
-
"Rename Included File" - rename the file in the #include directive and update all other #include directives of that file
-
"Move Function To Other File" - move a function to another file, automatically add an extern declaration in an appropriate header file and ensure that is included in the file where the function originally was
Using these automated refactorings it is much easier and safer to continuously maintain and improve the quality of any code base.
3.2. Options, option files and configuration
The current version of C-xrefactory allows only two possible sets of configuration/options.
The primary storage is (currently) the file $HOME/.c-xrefrc
which stores the "standard" options for all projects. Each project has
a separate section which is started with a section marker, the project
name surrounded by square brackets, [project1].
When you start c-xref you can use the command line option -xrefrc
to request that a particular option file should be used instead of the
"standard options".
When running the edit server there seems to be no way to
indicate a different options files for different
projects/files. Although you can start the server with -xrefrc you
will be stuck with that in the whole session and for all projects.
|
3.3. LSP
The LSP protocol is a common protocol for language servers such as
clangd and c-xrefactory. It allows an editor (client) to interface
to a server to request information, such as reference positions, and
operations, such as refactorings, without knowing exactly which server
it talks to.
Recent versions of c-xrefactory have an initial implementation of a
very small portion of the LSP protocol. The plan is to fully integrate
the functionality of c-xrefactory into the LSP protocol. This will
allow use of c-xrefactory from not only Emacs but also Visual Studio
Code or any other editor that supports the LSP protocol.
3.3.1. LSP Protocol Limitations
The LSP protocol was designed for single-shot, non-interactive operations. This creates constraints for c-xrefactory’s advanced refactorings:
Interactive Refactorings: C-xrefactory’s extract/parameter operations
require multi-step user input (names, positions, declarations). LSP’s
textDocument/codeAction doesn’t support interactive dialogs.
Symbol Browsing: C-xrefactory provides interactive symbol browsers with filtering and keyboard navigation. LSP returns flat reference lists with no standard for interactive UI.
Strategy: The LSP implementation aims to:
-
Provide basic IDE features (definition, completion, simple refactorings) to modern editors
-
Expose c-xrefactory’s advanced refactoring capabilities where possible
-
Keep the Emacs client as the primary interface for full interactive features
LSP serves to make c-xrefactory more accessible while the Emacs client probably will remain the gateway to its complete refactoring power.
4. Quality Attributes
The most important quality attributes are
-
correctness - a refactoring should never alter the behaviour of the refactored code
-
completness - no reference to a symbol should ever be missed
-
performance - a refactoring should be sufficiently quick so the user keeps focus on the task at hand
5. Constraints
TBD.
6. Principles
6.1. Reference Database and Parsing
The reference database is used only to hold externally visible identifiers to ensure that references to an identifier can be found across all files in the used source.
All symbols that are only visible inside a unit is handled by reparsing the file of interest.
This describes the semantics of the persisted snapshot (.cx files), not the
reference table in memory. The in-memory reference table holds all symbols encountered
during parsing, including file-local ones. Only externally visible symbols are persisted
to the snapshot because file-local symbols can always be reconstructed by reparsing. As
the architecture moves toward "memory as truth" (see Roadmap), the
distinction between "persisted" and "in-memory" symbols may evolve.
|
6.2. Terminology
The following terms are used throughout the documentation and codebase. Preferred terms are listed alphabetically; terms to avoid are noted to reduce ambiguity.
- Cold start
-
Server startup with no persisted snapshot available. All compilation units must be fully parsed to populate the reference table. Same code path as warm start, just more work.
- Compilation unit (CU)
-
A source file that is directly compiled (
.c,.y). Discovered by globbing the project directory. Distinguished from header files, which are included transitively and not compiled independently. - Include structure
-
The graph of
#includerelationships between files, represented in the reference table asTypeCppIncludereferences. Cheap to build (text scanning for#includelines). Separate from symbol references, which require full parsing. - Initialization
-
The first-request setup: discover project, load options, interrogate compiler, restore snapshot, scan project structure. Happens once per session. Not the same as cold start — initialization happens on every session, cold start describes the absence of a snapshot.
- Lightweight scan
-
Discovery of project structure by globbing for compilation units and text-scanning
#includelines, without full parsing. Populates the file table and include structure. Replaces-createand thecallXref()pre-refactoring pattern (ADR 22). - Persisted snapshot
-
The
.cxfiles on disk. A point-in-time copy of the reference table from a previous session, loaded at startup to avoid a full parse. May be stale — reconciled against the filesystem via mtime comparison.
Avoid "disk db", "cache", "reference database" when referring to the.cxfiles. A snapshot is not queryable (no search operations on disk), has no invalidation semantics (unlike a cache), and is not the source of truth (unlike a database). - Reference table
-
The authoritative in-memory state during a running session. Comprises the
referenceableItemTable(symbol references), the file table (file entries with modification tracking), andTypeCppIncludereferences (include structure). Populated by parsing, snapshot restoration, and lightweight scanning.
Avoid "in-memory db", "memory db". It is the live working set, not a database in the traditional sense. - Restoring
-
Loading a persisted snapshot into the reference table at startup. After restoration, mtime comparison determines which entries are fresh and which need reparsing.
Avoid "loading the database". - Saving / persisting
-
Writing the current reference table state to
.cxfiles. Only disk-file-derived references are persisted; references from unsaved editor buffers are excluded so that mtime-based validation remains correct at next startup.
Avoid "writing the database". - Staleness
-
A file is stale when its content has changed since it was last parsed. Detected by comparing
lastParsedMtimeagainst the current file modification time (from disk or editor buffer). Stale files trigger reparsing during the entry refresh (ADR 20). - Steady state
-
The server is initialized and processing requests. Staleness detection and incremental reparsing happen per-request. The reference table is authoritative.
Avoid "hot start" — ambiguous. - Symbol references
-
The detailed reference information (positions, usage types) for identifiers, created by full parsing. Expensive to produce. Distinguished from include structure, which is cheap.
- Entry refresh
-
The per-request mechanism that ensures the reference table is up-to-date before executing an operation. Covers both staleness (content was known but is now outdated) and unknown content (file discovered by scan but never parsed). Uses the include structure to determine what needs reparsing. Runs on every request in
callServer().
See Server Mode Flow in Code for implementation details. - Warm start
-
Server startup with an existing persisted snapshot. Most compilation units are fresh (snapshot mtime matches disk mtime); only stale ones need reparsing. Same code path as cold start, less work.
7. Software Architecture
7.1. Container View
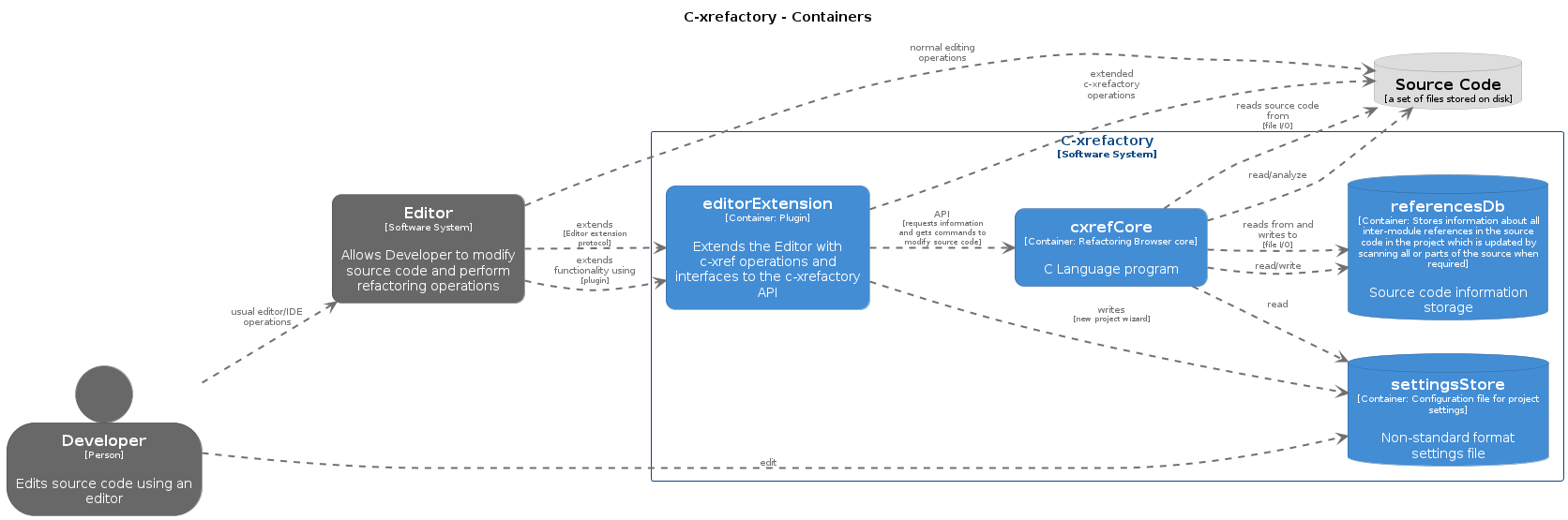
7.2. Containers
At this point the description of the internal structure of the containers are tentative. The actual interfaces are not particularly clean, most code files can and do include much every other module.
| There is still ongoing work is to try to identify modules/components, which are not always directly mapped to source files, but based on higher level responsibilites. |
7.2.1. CxrefProgram
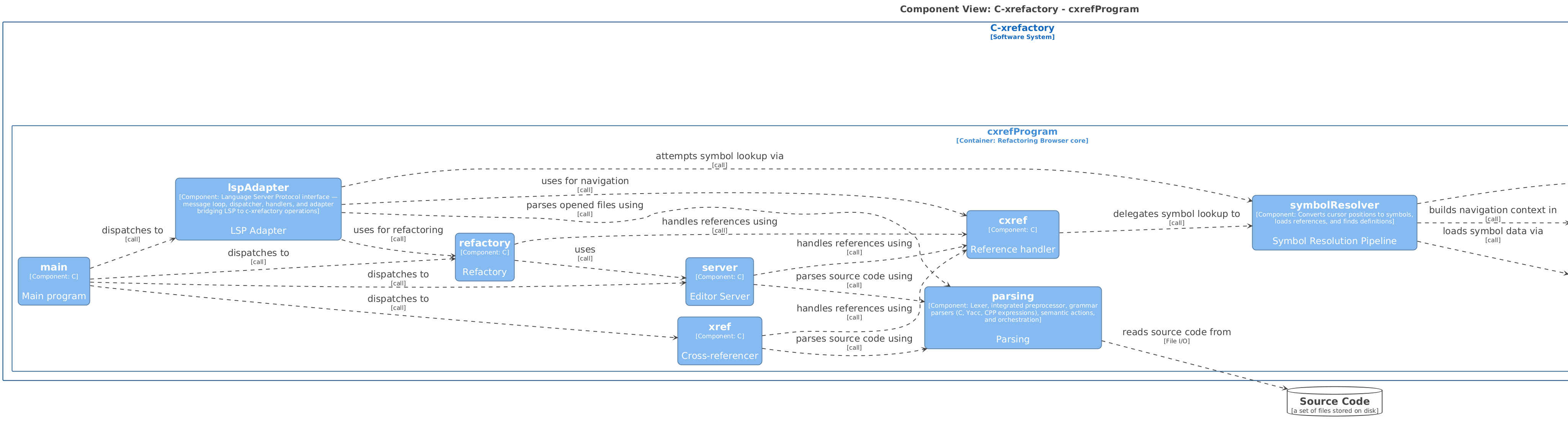
cxrefProgram is the core container. It does all the work when it comes
to finding and reporting references to symbols, communicating
refactoring requests as well as storing reference information for
longer term storage and caching.
Although c-xref can be used as a command line tool, which can be
handy when debugging or exploring, it is normally used in "server"
mode. In server mode the communication between the editor extension
and the 'cxrefProgram` container is a back-and-forth communication using a
non-standard protocol over standard pipes.
The responsibilities of cxrefProgram can largely be divided into
-
parsing source files to create, maintain the references database which stores all inter-module references
-
parsing source files to get important information such as positions for a functions begin and end
-
managing editor buffer state (as it might differ from the file on disc)
-
performing symbol navigation
-
creating and serving completion suggestions
-
performing refactorings such as renames, extracts and parameter manipulation
At this point it seems like refactorings are performed as separate
invocations of c-xref rather than through the server interface.
7.2.2. EditorExtension
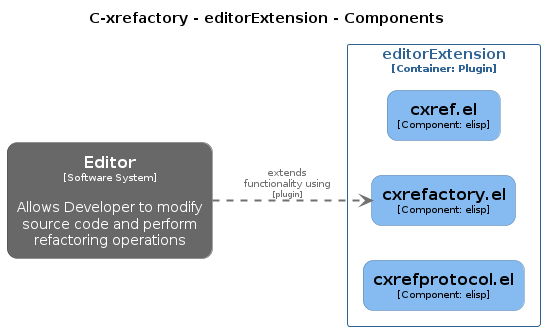
The EditorExtension container is responsible for plugging into an
editor of choice and handle the user interface, buffer management and
executing the refactoring edit operations.
Currently there is only one such extension supported, for Emacs,
although there existed code, still available in the repo history, for
an extension for jEdit which hasn’t been updated, modified or checked
for a long time and no longer is a part of this project.
There is a proof of concept implementation of a rudimentary LSP adapter which
would make it possible to use c-xrefactory from a wide range of editors and IDEs, at
least for many operations.
|
7.2.3. ReferencesDB
The References database stores crossreferencing information for symbols visible outside the module it is defined in. Information about local/static symbols are not stored but gathered by parsing that particular source file on demand.
Currently this information is stored in a somewhat cryptic, optimized text format.
This storage can be divided into multiple files, probably for faster access. Symbols are then hashed to know which of the "database" files it is stored in. As all crossreferencing information for a symbol is stored in the same "record", this allows reading only a single file when a symbol is looked up.
8. Components
This chapter describes the components of the cxrefProgram container, as defined in the C4 component diagram. Each section documents a component’s responsibilities, architecture, and interface.
Some components have clear boundaries and well-defined interfaces; others are still being separated from the legacy monolithic structure. The descriptions reflect the current state — what each component actually does today.
8.1. Parsing
8.1.1. Responsibilities
Parse C and Yacc source files, producing symbol references and semantic information for the reference database and for feature-specific operations (completion, extraction, refactoring).
8.1.2. Internal Structure
The parsing component consists of several internal modules:
-
Lexer and integrated preprocessor (
lexer.c,yylex.c) — transforms source text into lexem sequences, handles C preprocessor directives (macro definition and expansion, conditional compilation,#includeprocessing), and manages include file contexts by pushing and popping read states -
Grammar parsers — three yacc-generated parsers: C (
c_parser.y), Yacc (yacc_parser.y), and C preprocessor expressions (cppexp_parser.y) -
Semantic actions — modules that hook into grammar rules during parsing:
-
semact.c— core semantic actions: symbol tables, type checking, reference creation -
extract.c— feature semantic actions for extract refactoring (ifPARSE_TO_EXTRACT) -
complete.c— feature semantic actions for completion (ifPARSE_TO_COMPLETE)
-
-
Dispatch layer (
parsers.c) — selects the parser based on file language -
Configuration and orchestration (
parsing.c,parsing.h) — sets up parsing state and provides the external entry points
The integrated preprocessor is a key architectural choice: by implementing its own preprocessor rather than using the system’s, c-xrefactory can navigate to macro definitions, show macro usage, refactor macro names, and complete macro identifiers. The trade-off is imperfect compatibility with all compiler-specific preprocessor extensions.
8.1.3. Parser Operations
The parser’s behavior is configured through ParserOperation, decoupling parsing from server-level concerns:
| Operation | Purpose |
|---|---|
|
Standard parse: create symbol references in the in-memory reference table |
|
Build completion candidates at cursor position |
|
Track blocks, variables, and control flow for extract refactoring |
|
Record function start/end positions |
|
Check if a position is a valid move-function target |
|
Track parameter positions for argument manipulation |
The server maps its ServerOperation to a ParserOperation via getParserOperation(), so the parser never needs to know about server-level operation enums.
8.1.4. Parser Generation
The parsers are generated using a patched Berkeley yacc (byacc-1.9). The patch modifies the skeleton to support error recovery and a recursive parsing feature (originally for Java). CPP macros rename parser data structures so that multiple parsers can coexist in the same executable. The Makefile generates and renames the parser output files.
8.1.5. Interface
Key entry points (see parsing.h):
// Parse a file and create references in the in-memory table
void parseToCreateReferences(const char *fileName);
// Configure parsing for a specific file (sets language, includes, etc.)
void setupParsingConfig(int fileNumber);
// Dispatch to the appropriate parser
void callParser(int fileNumber, Language language);parseToCreateReferences() is the clean entry point used by LSP mode, the entry-point reparse loop, and navigation refresh. It takes a filename, determines the language, sets up configuration, and parses.
callParser() is the lower-level dispatch used by server mode’s parseInputFile(), where configuration is set up separately with cursor position and operation-specific state.
8.2. Xref
8.2.1. Responsibilities
Build and update the on-disk cross-reference database (.cx files) by parsing all scheduled project files. The xref component is the batch counterpart to the interactive server: where the server processes one file per editor request, xref processes all project files in a single invocation.
8.2.2. Operations
-
Create (
-create): Parse every project file from scratch, generate the full.cxdatabase -
Fast update (
-update): Re-parse only files whose modification time has changed -
Full update (
-update -fullupdate): Re-parse modified files and their include closure — all compilation units that transitively include a modified header (makeIncludeClosureOfFilesToUpdate())
8.2.3. Memory Overflow Handling
When the in-memory reference table overflows mid-parse, xref flushes the accumulated references to disk via saveReferences(), recovers memory, and continues parsing the remaining files. This setjmp/longjmp-based overflow mechanism allows xref to handle projects larger than available memory.
8.2.4. Interface
void xref(ArgumentsVector args); // Top-level entry: open output, load buffers, call callXref, save
void callXref(ArgumentsVector args, XrefConfig *config); // Core loop: schedule files, parse all, save referencescallXref() is also called by the refactory to re-index files after refactoring operations.
8.3. Server
8.3.1. Responsibilities
Serve the editor extension by processing requests in an infinite loop. Each request is a set of command-line-style options received over stdin. The server:
-
Dispatches operations (navigation, completion, refactoring support, project management)
-
Ensures all operations see fresh in-memory references by reparsing stale files at the entry point
-
Manages the browsing session stack for navigation operations
-
Coordinates with the parser subsystem to process input files
8.3.2. Request Lifecycle
The server runs as a long-lived process started by the editor (c-xref -server). Communication is over stdin/stdout using a text protocol where commands look like command-line options.
server() — infinite request loop [server.c]
│
└─> FOR EACH REQUEST:
├─> Read options from pipe
├─> initServer() — process options, schedule input file
├─> callServer() — main dispatch
│ ├─> loadAllOpenedEditorBuffers()
│ ├─> Reparse stale preloaded files (Pass 1: CUs, Pass 2: header includers)
│ ├─> prepareInputFileForRequest()
│ ├─> FIRST REQUEST (GetProject):
│ │ ├─ initializeProjectContext()
│ │ ├─ processFileArguments() — discover CUs by globbing project dir
│ │ ├─ loadFileNumbersFromStore() — load .cx snapshot into file table
│ │ └─ parseDiscoveredCompilationUnits() — parse stale CUs, skip fresh
│ ├─> Dispatch based on operation:
│ │ ├─ Operations needing input file → processFile() → parse
│ │ └─ Other operations (filter, pop, etc.)
│ └─> Navigation operations use browsing stack
├─> answerEditorAction() — send response to editor
└─> Cleanup (close buffers, close output)8.3.3. Entry-Point Reparse (ADR 20)
Before dispatching any operation, the server reparses stale preloaded files so that all operations see fresh in-memory references. This separates the concern of "keeping data fresh" from individual operation logic.
The entry-point reparse loop:
-
Iterates all editor buffers (files preloaded from the editor)
-
For each stale compilation unit (
.c,.y— determined byisCompilationUnit()): reparses the file, updateslastParsedMtime, and setsneedsBrowsingStackRefreshon theFileItem -
For each stale header: walks the reverse-include graph (via
TypeCppIncludereferences) to find compilation units that transitively include it, and reparses those CUs -
Sets
options.cursorOffset = -1during reparse to prevent the lexer from triggering on-line action handling
The needsBrowsingStackRefresh flag bridges the entry-point (which handles parsing) and the navigation module (which handles browsing stack updates). Navigation checks this flag instead of fileNumberIsStale() and calls updateSessionReferencesForFile() to update only the browsing stack without re-parsing.
After a browsing stack refresh, the server restores its position by finding the nearest reference to where it was, then advances (NEXT) or retreats (PREVIOUS) in list order. This respects the definition-first navigation ordering without assuming any particular sort order.
8.3.4. File Discovery and the File Table
The server can only reparse and navigate files it knows about. "Knowing" a file means it has an entry in the file table — a file number and metadata (FileItem). But being known does not mean being parsed: a file in the table may have no references in the referenceableItemTable yet. This distinction matters because the entry-point reparse loop, the reverse-include graph walk, and navigation all operate only on known files.
Files enter the file table through three mechanisms:
Disk database (loadFileNumbersFromStore()). On the first request that triggers project initialization, the server loads file numbers from the .cx database. This is why -create was historically required before any interactive use: it populated the persistent database that seeds the file table. Without it, the server would only know about the single file in the current request.
Editor preloads. When the editor sends -preload <file> <tmpfile>, the file enters the file table via the editor buffer mechanism. Files created during a session — new source files the user opens — are discovered this way without any explicit rescan.
Project directory glob (processFileArguments()). At startup, after project context initialization, the server walks options.inputFiles (typically ., the project root) recursively, filtering by known source suffixes (.c, .y, etc.) and honoring -prune paths. This discovers all compilation units in the project directory without requiring a prior -create invocation.
The three mechanisms are complementary: the disk database provides historical knowledge, preloads provide real-time updates during the session, and the project directory glob provides a fresh scan of what actually exists on disk at startup.
Design boundary: Files that appear on disk but are not in the file table — because they weren’t in the disk database, weren’t opened in the editor, and weren’t present at startup — are invisible to the server until the next session. The startup glob combined with editor preloads covers the primary use cases: all project files are discovered at startup, and new files created during the session enter through the editor.
8.3.5. Operation Classification
Operations are classified by what they need:
-
Needs reference database (
needsReferenceDatabase): navigation, refactoring support, unused symbol detection — these push a browsing session -
Requires input file processing (
requiresProcessingInputFile): completion, search, extraction, and all reference-database operations — these parse the request’s input file -
Neither: project management, filter changes, browsing stack manipulation — these operate on existing session state
8.3.6. Interface
void server(ArgumentsVector args); // Infinite request loop
void callServer(ArgumentsVector baseArgs, ArgumentsVector requestArgs); // Single request dispatch
void initServer(ArgumentsVector args); // Per-request initialization8.4. LSP Adapter
8.4.1. Responsibilities
Implement the Language Server Protocol interface, allowing LSP-capable editors (VS Code, Emacs lsp-mode, etc.) to use c-xrefactory’s parsing and navigation capabilities. Currently at proof-of-concept stage with partial textDocument/definition support.
8.4.2. Internal Structure
The LSP adapter is a self-contained subsystem with clear internal layering:
-
Message loop (
lsp.c) — reads LSP framed messages (Content-Length headers + JSON body) from stdin, delegates to the dispatcher, and runs until shutdown/exit -
Dispatcher (
lsp_dispatcher.c) — maps LSP method strings ("textDocument/definition","initialize", etc.) to handler functions via a static dispatch table -
Handlers (
lsp_handler.c) — implement individual LSP requests and notifications:initialize(sets up file table, editor buffers, parsing subsystem, and reference database),textDocument/didOpen(loads file content and parses it),textDocument/definition(delegates to adapter),shutdown/exit(cleanup) -
Adapter (
lsp_adapter.c) — bridges LSP concepts to c-xrefactory internals.findDefinition()converts LSP URI and position to an internalPosition, queries theReferenceDatabase, and returns an LSP location JSON object -
Sender (
lsp_sender.c) — formats and sends JSON responses with Content-Length framing -
Utilities (
lsp_utils.c) — coordinate conversions: URI to file path, LSP line/character to byte offset and back
8.4.3. Architectural Differences from Server Mode
The LSP adapter takes a fundamentally different approach from the legacy editor server:
| Aspect | Server Mode | LSP Mode |
|---|---|---|
Protocol |
Custom text protocol (command-line options over pipe) |
Standard LSP (JSON-RPC over Content-Length framing) |
Initialization |
Relies on pre-existing |
Builds in-memory reference database from scratch via parsing |
File handling |
Editor sends preloads; server uses file table scheduling |
|
Entry point |
|
|
8.4.4. Current Limitations
The LSP adapter is a proof-of-concept. Key gaps:
-
Only
textDocument/definitionpartially works — and only for files that have been opened (parsed) in the current session -
No incremental updates: modifying a file after opening does not re-parse
-
No project-wide indexing: symbols from unopened files are invisible
-
The
ReferenceDatabaseabstraction is minimal and separate from the legacy in-memory reference table
8.4.5. Interface
// Top-level entry: detect -lsp flag and run the LSP message loop
bool want_lsp_server(ArgumentsVector args);
int lsp_server(FILE *input);
// Adapter: bridge LSP requests to c-xrefactory operations
JSON *findDefinition(const char *uri, JSON *position);8.5. Refactory
8.5.1. Responsibilities
Coordinate refactoring operations: rename, move, extract, and argument manipulation. The refactory component receives a refactoring request, uses the parser and reference database to analyze the code, performs safety checks, and produces a sequence of edits for the editor to apply.
8.5.2. Invocation Model
Refactoring operations run as a separate c-xref invocation, not through the long-lived editor server. The editor starts a new c-xref process with -refactory and the specific refactoring flag (e.g. -rfct-rename, -rfct-extract-function). This separate process communicates results back via the protocol and exits when done.
This design means the refactoring process has its own option state (refactoringOptions), separate from the server’s. The check options.refactoringRegime == RegimeRefactory gates refactoring-specific code paths.
8.5.3. Operation Flow
A typical refactoring (e.g. rename):
-
Editor invokes
c-xref -refactory -rfct-rename -renameto=NEW_NAME -olcursor=POSITION FILE -
Refactory parses the file to identify the symbol at the cursor
-
Safety checks verify the rename is valid (no collisions, scope analysis)
-
For each occurrence: sends
<goto>+<precheck>to verify the editor’s file matches -
Sends
<replacement>instructions for each occurrence -
Editor applies the edits
8.5.4. Safety Checks
Before applying a refactoring, the refactory performs safety checks (OP_INTERNAL_SAFETY_CHECK). These use the reference database to verify that the transformation is semantically valid — for example, that a rename won’t collide with an existing symbol in scope.
8.6. Extract
8.6.1. Responsibilities
Analyze control flow for extract-function/macro/variable refactoring. The extract component operates in two phases: collection during parsing (registers synthetic labels, gathers references) and analysis after parsing (classifies variables, generates output).
8.6.2. Operation
Extraction uses a specialized parse operation (PARSE_TO_EXTRACT) that tracks:
-
Block structure and nesting
-
Variable definitions and uses within the selection
-
Control flow (return, break, continue) crossing the extraction boundary
After parsing, it classifies variables as inputs (passed as parameters), outputs (returned), or local (moved into the extracted function), and generates the function signature, call site, and body.
8.7. Cxref
8.7.1. Responsibilities
Manage the in-memory symbol reference tables and the browsing session stack. The cxref component is the runtime engine for symbol lookup: it loads references from the on-disk database (via cxfile), merges them with freshly parsed references, and provides the data structures that navigation and refactoring operations query.
The component boundary is not yet clean. Parts of this functionality are spread across cxref.c, session.c, navigation.c, and referenceableitemtable.c. The description below reflects the logical responsibilities, not a single module.
|
8.7.2. Architecture Overview
c-xrefactory’s core functionality relies on a symbol database that stores cross-references, definitions, and usage information for all symbols in a project. The database has two forms:
-
On-disk (
.cxfiles) — persistent, hash-partitioned symbol records managed by the Cxfile component -
In-memory (reference tables) — runtime tables populated by parsing and by loading from
.cxfiles
8.7.3. Key Data Structures
Browsing Stack (sessionData.browsingStack)
The browsing stack is the runtime data structure for symbol navigation. Each push operation (triggered by a navigation request) creates a new session entry containing the references for the symbol under the cursor.
Referenceable Items
A ReferenceableItem represents a symbol (function, variable, macro, type, etc.) with its attributes: link name, type, storage class, scope, and visibility. Each referenceable item has a linked list of Reference entries recording every usage position.
References
A Reference records a single occurrence of a symbol: file, line, column, and usage kind (defined, declared, used, etc.). References are the fundamental unit that navigation, unused-symbol detection, and refactoring operate on.
8.7.4. Symbol Resolution Flow
When the user requests "go to definition" for a symbol:
-
Parse the current file to identify the symbol at cursor position
-
Load symbol data from
.cxfiles (via cxfile) into the browsing stack -
Merge with any in-memory references from recently parsed files
-
Order references by usage priority (definition > declaration > usage)
-
Navigate to the best definition position
8.7.5. Database Operations
-
Create (
-create): Parse all project files, generate reference items, write to.cxfiles -
Update (
-update): Re-parse modified files (with include-closure expansion for full updates), merge into existing database -
Query (server operations): Load symbol data from
.cxfiles into the browsing stack for navigation
8.8. Main
8.9. Memory
8.9.1. Responsibilities
The Memory module provides arena-based allocation for performance-critical and request-scoped operations:
-
Fast allocation for macro expansion and lexical analysis
-
Bulk deallocation for request-scoped cleanup
-
Multiple specialized arenas for different data lifetimes
-
Overflow detection and optional dynamic resizing
8.9.2. Design Rationale
Historical Context
In the 1990s when c-xrefactory originated, memory was scarce. The design had to:
-
Minimize allocation overhead (no malloc/free per token)
-
Support large projects despite limited RAM
-
Allow overflow recovery via flushing and reuse
-
Enable efficient bulk cleanup
Most memory arenas use statically allocated areas. Only cxMemory supports dynamic resizing to handle out-of-memory situations by discarding, flushing and reusing memory. This forced implementation of a complex caching strategy since overflow could happen mid-file.
Modern Benefits
Even with abundant modern memory, arena allocators provide:
-
Performance: Bump pointer allocation is ~10x faster than malloc
-
Cache locality: Related data allocated contiguously
-
Automatic cleanup: Bulk deallocation prevents leaks
-
Request scoping: Natural fit for parsing/expansion operations
8.9.3. Arena Types and Lifetimes
| Arena | Purpose | Lifetime |
|---|---|---|
cxMemory |
Symbol database, reference tables, cross-reference data |
File or session |
ppmMemory |
Preprocessor macro expansion buffers (temporary allocations) |
Per macro expansion |
macroBodyMemory |
Macro definition storage |
Session |
macroArgumentsMemory |
Macro argument expansion |
Per macro invocation |
fileTableMemory |
File metadata and paths |
Session |
optMemory |
Command-line and config option strings (with special pointer adjustment) |
Session |
8.9.4. Key Design Patterns
Marker-Based Cleanup
Functions save a marker before temporary allocations:
char *marker = ppmAllocc(0); // Save current index
// ... temporary allocations ...
ppmFreeUntil(marker); // Bulk cleanupBuffer Growth Pattern
Long-lived buffers that may need to grow:
// Allocate initial buffer
bufferDesc.buffer = ppmAllocc(initialSize);
// ... use buffer, may need growth ...
// Free temporaries FIRST
ppmFreeUntil(marker);
// NOW buffer can grow (it's at top-of-stack)
expandPreprocessorBufferIfOverflow(&bufferDesc, writePointer);Overflow Handling
The cxMemory arena supports dynamic resizing:
bool cxMemoryOverflowHandler(int n) {
// Attempt to resize arena
// Return true if successful
}
memoryInit(&cxMemory, "cxMemory", cxMemoryOverflowHandler, initialSize);When overflow occurs, handler can:
-
Resize the arena (if within limits)
-
Flush old data and reset
-
Signal failure (fatal error)
8.9.5. Interface
Key functions (see memory.h):
// Initialization
void memoryInit(Memory *memory, char *name,
bool (*overflowHandler)(int n), int size);
// Allocation
void *memoryAlloc(Memory *memory, size_t size);
void *memoryAllocc(Memory *memory, int count, size_t size);
// Reallocation (only for most recent allocation)
void *memoryRealloc(Memory *memory, void *pointer,
size_t oldSize, size_t newSize);
// Bulk deallocation
size_t memoryFreeUntil(Memory *memory, void *marker);
// Guards
bool memoryIsAtTop(Memory *memory, void *pointer, size_t size);8.9.6. Common Pitfalls
See the "Arena Allocator Lifetime Violations" section in the Development Environment chapter for:
-
Attempting to resize buffers not at top-of-stack
-
Calling
FreeUntil()too late -
Mixing arena lifetimes
8.9.7. Future Directions
Modern systems have abundant virtual memory. Possible improvements:
-
Simplify overflow handling - Allocate larger initial arenas
-
Separate lifetime management - Don’t mix temporary and long-lived allocations
-
Consider alternatives - Linear allocators for some use cases
-
Add debug modes - Track allocation patterns and detect violations
The experimental FlushableMemory type explores some of these ideas but hasn’t replaced current implementation.
8.10. Content Buffers (EditorBuffer)
8.10.1. Responsibilities
Content buffers provide an in-memory cache of file content that transparently overrides disk file reading during parsing. When a content buffer exists for a file, the parser uses its in-memory content instead of reading from disk.
8.10.2. Three Roles
Content buffers (the EditorBuffer struct) serve three distinct roles:
| Role | preLoadedFromFile |
How content arrives |
|---|---|---|
Editor content |
Non-NULL (tmp file path) |
Client writes unsaved buffer to a tmp file; server reads the tmp file. Content represents the editor’s in-memory state, which may differ from the original file on disk. |
Disk file cache |
NULL |
Created on demand by |
LSP document state |
NULL |
Content arrives in a |
8.10.3. How Parsing Uses Buffers
The lexer reads from a character buffer (currentFile.characterBuffer), which is the common layer regardless of content source. Where the character buffer gets its data depends on whether a content buffer exists:
-
Content buffer path:
initInputFromEditorBuffer()points the character buffer directly into the content buffer’s text memory. All content is available immediately — no file I/O. -
File path:
initInputFromFile()usescurrentFile.characterBuffer.chars— a separate fixed-size buffer. Data is read from the FILE handle incrementally as the lexer consumes characters.
When the lexer processes an #include, it calls findOrCreateAndLoadEditorBufferForFile() for the included file. This function:
-
Checks if a content buffer already exists (preloaded or cached) — if so, returns it
-
Otherwise reads the file from disk into a new content buffer
If a content buffer is found, the character buffer is set up to read from it. If not (file doesn’t exist or is a directory), the fallback openFile() path reads from disk via a FILE handle. This means preloaded editor content transparently overrides disk content — the parser doesn’t know or care where the content came from.
8.10.4. Lifetime
Buffer lifetime depends on the server mode and buffer role:
| Context | Behavior |
|---|---|
Server mode, editor content |
Currently destroyed after each request ( |
Server mode, disk cache |
Destroyed after each request. Appropriate since different requests may parse different files. |
Xref mode, disk cache |
Preserved across file processing ( |
LSP mode, document state |
Persistent from |
The existing bufferIsCloseable() predicate distinguishes these cases: it returns false for preloaded buffers (preserving editor content) and true for loaded, unmodified, marker-free buffers (allowing cache cleanup).
8.10.5. Staleness Detection
For preloaded buffers, staleness is detected by comparing fileItem→lastParsedMtime with buffer→modificationTime. After parsing a preloaded buffer, lastParsedMtime is set to the buffer’s modification time. If the buffer is re-sent with a new tmp file (new mtime), the file appears stale and is reparsed.
See the Server component’s Entry-Point Reparse section for how staleness drives the sync phase.
8.11. Cxfile
8.11.1. Responsibilities
Read and write the CXref database (.cx files) in a compact text format. Cxfile is the persistence layer: it serializes symbol references to disk after parsing and loads them back during navigation and refactoring operations.
8.11.2. Database Structure
The database uses a hash-partitioned file structure:
cxrefs/
├── files # File metadata and paths
├── 0000 # Symbol data for hash bucket 0
├── 0001 # Symbol data for hash bucket 1
└── ... # Additional hash buckets (count set by -refnum)All information about a symbol is stored in exactly one file, determined by hashing its link name. This means a single file read suffices to look up any symbol.
8.11.3. File Format
Records use the general format <number><key>[<value>]. The encoding uses single-character markers listed at the top of cxfile.c.
The coding often starts with a number followed by a character key: 4l means line 4, 23c means column 23. References are optimized to avoid repeating fields that haven’t changed — so 15l3cr7cr means two references on line 15, one at column 3, the other at column 7 (using fsulc fields: file, symbol index, usage, line, column).
Some fields carry a length prefix: filenames use <length>:<path> (e.g. 84:/home/…/file.c), version strings use <length>v.
Example file information line:
32571f 1715027668m 21:/usr/include/ctype.h
-
32571f— file number 32571 -
1715027668m— modification time (to detect stale entries) -
21:/usr/include/ctype.h— filename (21 characters)
8.11.4. Reading
Reading is controlled by scanFunctionTable arrays. Each entry maps a record key to a handler function. As the reader encounters a key in the file, it looks up the handler and calls it. This table-driven approach allows different consumers to register for different record types — for example, loading only symbol names vs. loading full reference lists.
8.12. Editor Extension
The Emacs editor extension is implemented in these components/files:
-
c-xref.el
-
c-xrefactory.el
-
c-xrefprotocol.el (auto-generated)
8.12.1. Responsibilities
The Emacs client extension provides the user-facing interface for navigation, refactoring, and completion. It starts the c-xref process on the first user interaction and communicates with the server process over stdin/stdout using a text protocol.
8.12.2. Preloading
To give the server access to unsaved content the client sends -preload <file> <tmpfile> for modified editor. On PUSH, NEXT, and PREVIOUS, all modified buffers (including the current one if modified) are preloaded. Unmodified buffers are not preloaded — the server reads the disk file directly.
The preload mechanism writes the buffer content to a temporary file and passes both the original filename and the temp file path. The server creates an EditorBuffer with the content and the temp file’s modification time. After each request, all editor buffers are closed (closeAllEditorBuffers), so preloads are re-sent on every request.
== Implementation Notes
This chapter collects cross-cutting implementation details that don’t belong to a single component: editor-server protocol, file processing orchestration, multi-pass configuration, and other observations about how the subsystems interact.
8.13. Commands
The editorExtension calls the server using command line
options. These are then converted to first a command enum starting in
OP ("operation") or AVR ("available refactoring").
Some times the server needs to call the crossreferencer which is
performed in the same manner, command line options, but this call is
internal so the wanted arguments are stored in a vector which is
passed to the xref() in the same manner as main() passes the
actual argc/argv.
Many of the commands require extra arguments like positions/markers
which are passed in as extra arguments. E.g. a rename requires the
name to rename to which is sent in the renameto= option, which is
argparsed and stored in the option structure.
Some of these extra arguments are fairly random, like -olcxparnum=
and -olcxparnum2=. This should be cleaned up.
A move towards "events" with arguments would be helpful. This would mean that we need to:
-
List all "events" that
c-xrefneed to handle -
Define the parameters/extra info that each of them need
-
Clean up the command line options to follow this
-
Create event structures to match each event and pass this to
server,xrefandrefactory -
Rebuild the main command loop to parse command line options into event structures
8.14. Passes
c-xrefactory makes it possible to parse the analyzed source multiple passes in case
you compile the project sources with different C defines. In the project configuration
file you specify `-passN' followed by the settings, typically C PreProcessor defines,
that are to be applied for this pass over the sources.
8.15. File Processing Orchestration
The file processing architecture differs significantly between Server mode, Xref mode, and LSP mode, with confusing global state and naming inconsistencies that make the code hard to follow.
The current architecture is being restructured toward a unified server flow where
lightweight file structure scanning replaces the legacy -create/callXref() pattern.
See Target: Unified Server Flow (ADR 22) below and ADR 22 for the target design. Annotations marked
[TARGET] indicate planned changes.
|
8.15.1. File Scheduling - How Files Get Marked for Processing
All modes begin by marking files for processing using the isScheduled flag in the file table.
Initial Scheduling (All Modes)
Called from:
-
Server:
initServer()→processFileArguments()[server.c:151] -
Xref:
mainTaskEntryInitialisations()→processFileArguments()[startup.c:706]
Flow:
processFileArguments() [options.c:1893]
│
└─> FOR each file in options.inputFiles
│
└─> processFileArgument(filename) [options.c:1864]
│
└─> dirInputFile(...) [options.c:465]
├─ If directory: recursively map over files
├─ If file: scheduleCommandLineEnteredFileToProcess(filename)
│ └─ SETS: fileItem->isScheduled = true [line 450]
└─ If wildcard: expand and recurseResult: All command-line files (and directory contents if -r flag) are marked with isScheduled = true.
[TARGET] processFileArguments() will be replaced by scanProjectForFilesAndIncludes(),
which discovers CUs by globbing the project directory rather than relying on command-line
file lists. This also builds the include graph transitively by text-scanning #include
lines and resolving paths via options.includeDirs. See Target: Unified Server Flow (ADR 22).
Additional Update Scheduling (Xref Mode Only)
Called from: callXref() → scheduleModifiedFilesToUpdate() [xref.c:296]
Flow:
scheduleModifiedFilesToUpdate(isRefactoring) [xref.c:207]
│
├─> mapOverFileTable(schedulingToUpdate, isRefactoring)
│ └─ For each file: if modified, SETS: fileItem->scheduledToUpdate = true
│
├─> If UPDATE_FULL: makeIncludeClosureOfFilesToUpdate()
│ └─ Expands scheduledToUpdate to include all files that #include updated files
│
└─> mapOverFileTable(schedulingUpdateToProcess)
└─ For each file: if (scheduledToUpdate && isArgument)
SETS: fileItem->isScheduled = true [line 115]Result: In update mode, only modified files (and their includers) get isScheduled = true.
8.15.2. Server Mode Flow
SINGLE FILE PER REQUEST - Server processes one file per request.
server() - Infinite request loop
│
└─> FOR EACH REQUEST:
│
└─> callServer(baseArgs, requestArgs, &firstPass)
│
├─> loadAllOpenedEditorBuffers()
│
├─> prepareInputFileForRequest()
│ └─ SETS: requestFileNumber
│
├─> IF NOT projectContextInitialized (one-time):
│ ├─ OP_ACTIVE_PROJECT: initializeProjectContext()
│ │ → loadFileNumbersFromStore()
│ │ → Legacy: processFileArguments()
│ │ + parseDiscoveredCompilationUnits()
│ └─ SETS: projectContextInitialized = true
│
├─> Config-change-aware scan (auto-detect only):
│ ├─ IF config changed: reloadProjectConfig()
│ │ → re-reads .c-xrefrc, updates options.includeDirs
│ └─ IF !scanDone OR config changed:
│ scanProjectForFilesAndIncludes()
│ + markMissingFilesAsDeleted()
│ SETS: scanDone = true
│
├─> Entry refresh (if projectContextInitialized):
│ ├─ Pass 1: reparse stale CUs directly
│ ├─ Pass 2: find CUs that include stale headers
│ │ (via TypeCppInclude refs), reparse those
│ └─ Pass 3: find unparsed CUs that share headers with
│ the request file, parse those
│
└─> Dispatch operation
├─ requiresProcessingInputFile: processFile()
└─ other: unschedule fileThe entry refresh (see Terminology in Principles) ensures
the reference table is up-to-date before each operation. Pass ordering is critical:
Pass 1 reparses stale CUs, which updates their TypeCppInclude references. Pass 2
then queries those freshened references to find which CUs include stale headers. Pass 3
uses the include structure from the lightweight scan to find CUs sharing headers with
the request file that have never been parsed. A user cannot create a new include edge
without editing the includer, so the includer is always stale when the edge is new.
The per-request dispatch still follows the legacy pattern:
└─> processFile(baseArgs, requestArgs, &firstPass) [server.c:199]
├─ SETS: inputFileName = fileItem->name [line 205]
│
└─> singlePass(args, nargs, &firstPass) [server.c:155]
│
├─> initializeFileProcessing(args, nargs, &firstPass) [startup.c:490]
│ ├─ READS: fileName = inputFileName [line 502]
│ ├─ USES: parsingConfig.fileNumber = currentFile.characterBuffer.fileNumber [line 161]
│ │
│ └─> computeAndOpenInputFile(inputFileName) [startup.c:112]
│ ├─ Gets EditorBuffer or opens file
│ │
│ └─> initInput(inputFile, inputBuffer, "\n", fileName) [yylex.c]
│ └─ Sets up currentFile global with CharacterBuffer
│
├─> parseInputFile() [server.c:131]
│ ├─ USES: currentFile.fileName [line 133]
│ ├─ Calls setupParsingConfig(requestFileNumber) [line 136]
│ │
│ └─> callParser(parsingConfig.fileNumber, parsingConfig.language) [line 140]
│
└─> SPECIAL CASE: Completion in macro body [lines 183-196]
├─ SETS: inputFileName = getFileItemWithFileNumber(...)->name [line 189]
├─> initializeFileProcessing(args, nargs, &firstPass) [again]
└─> parseInputFile() [again]8.15.3. Xref Mode Flow
PROCESSES ALL SCHEDULED FILES - Xref creates a list of all scheduled files and processes them in a loop.
xref(args) [xref.c:354]
│
└─> callXref(args, isRefactoring) [xref.c:283]
│
├─> IF options.update:
│ └─> scheduleModifiedFilesToUpdate(isRefactoring) [line 296]
│ └─ Adds modified files to scheduled list
│
├─> fileItem = createListOfInputFileItems() [line 298]
│ └─ Creates linked list of ALL scheduled files (sorted by directory)
│
└─> FOR LOOP over fileItem list [line 314]
│
└─> oneWholeFileProcessing(args, fileItem, &firstPass, ...) [xref.c:179]
├─ SETS: inputFileName = fileItem->name [line 181]
│
└─> processInputFile(args, &firstPass, &atLeastOneProcessed) [xref.c:149]
│
├─> initializeFileProcessing(args, nargs, &firstPass) [startup.c:490]
│ ├─ READS: fileName = inputFileName [line 502]
│ │
│ └─> computeAndOpenInputFile(inputFileName) [startup.c:112]
│ └─> initInput(inputFile, inputBuffer, "\n", fileName) [yylex.c]
│ └─ Sets currentFile.characterBuffer.fileNumber
│
├─ SETS: parsingConfig.fileNumber = currentFileNumber [line 160]
│ (NOTE: currentFileNumber is DIFFERENT global!)
│
└─> parseToCreateReferences(inputFileName) [parsing.c:165]
├─ Gets EditorBuffer using fileName parameter
│
├─> initInput(NULL, buffer, "\n", fileName) [line 181]
│ └─ DUPLICATE call! Already called in initializeFileProcessing!
│
├─ Calls setupParsingConfig(currentFile.characterBuffer.fileNumber) [line 183]
│
└─> callParser(parsingConfig.fileNumber, parsingConfig.language) [line 190]8.15.4. LSP Mode Flow (New, Simplified)
parseToCreateReferences(fileName) [parsing.c:165]
├─ Takes fileName as PARAMETER (not from global!)
├─ Gets EditorBuffer
│
├─> initInput(NULL, buffer, "\n", fileName) [line 181]
│ └─ Sets currentFile.characterBuffer.fileNumber
│
├─> setupParsingConfig(currentFile.characterBuffer.fileNumber) [line 183]
│
└─> callParser(parsingConfig.fileNumber, parsingConfig.language) [line 190]8.15.5. Key Observations
Assignments to `inputFileName`
Server Mode: Set once per file processed
-
processFile()line 205 - sets the file for the current request -
Special case: macro completion may parse a different file (line 189) to resolve symbols in unexpanded macro bodies
Xref Mode: Set ONCE per file
-
oneWholeFileProcessing()line 181
`requestFileNumber` Only Used in Server Mode
-
Set in
prepareInputFileForRequest()(lines 104, 121) -
Used in
parseInputFile()line 136:setupParsingConfig(requestFileNumber) -
NOT used in Xref mode at all
Confusion: THREE Different File Number Globals!
inputFileName // The file name being processed
requestFileNumber // Server: file number from scheduled file (server.c)
currentFileNumber // Xref: file number after parsing starts (parsing.c:26)In xref.c line 160:
parsingConfig.fileNumber = currentFileNumber;But currentFileNumber is defined in parsing.c:26:
int currentFileNumber = -1; /* Currently parsed file, maybe a header file */The comment reveals the distinction: currentFileNumber can change DURING parsing when entering #include files, while requestFileNumber stays constant as "the file we were asked to process."
Double initInput() Call in Xref Mode
In Xref mode, initInput() is called TWICE for the same file:
-
First in
initializeFileProcessing()→computeAndOpenInputFile()[startup.c:128] -
Second in
parseToCreateReferences()[parsing.c:181]
This appears to be a bug or wasteful duplication.
`initializeFileProcessing` is Heavy Orchestration
This 500-line function does five major phases:
-
Phase 1: Project discovery (find
.c-xrefrc) -
Phase 2: Options processing
-
Phase 3: Compiler interrogation (expensive! runs
gcc -v) -
Phase 4: Memory checkpointing (to skip Phase 3 for same-project files)
-
Phase 5: Finally calls
computeAndOpenInputFile()→initInput()
The firstPass parameter gates Phase 4’s memory checkpoint save/restore.
[TARGET] initializeProjectContext will be eliminated — it duplicates phases 1-4 of
initializeFileProcessing. With the unified flow, all initialization goes through
loadProjectSettings() once at startup. The multi-project fast-path optimization
(checkpoint restore when same project) becomes dead code with single-project servers
(ADR 21).
Naming Inconsistency
-
inputFileName- used in both Server and Xref modes, but set in different places -
requestFileNumber- only Server mode, represents the file from the request -
currentFileNumber- only Xref mode(?), set byinitInput()after file opened
If they represent the same concept (the file being processed), they should have parallel names.
8.15.6. Summary: Multi-File vs Single-File Processing
Server Mode - Single File Per Request
-
Scheduling: All files scheduled ONCE in
initServer()→processFileArguments() -
Processing: Each request picks ONE file via
prepareInputFileForRequest()-
Uses
getNextScheduledFile()to get first scheduled file -
FLAWED: unschedules all higher-numbered files (works because
c-xref .schedules all) -
Sets both
inputFileNameandrequestFileNumber
-
-
Loop: Infinite request loop in
server()- different file per request
Xref Mode - All Files Per Invocation
-
Scheduling: All files scheduled in
mainTaskEntryInitialisations()→processFileArguments() -
Additional: In update mode,
scheduleModifiedFilesToUpdate()adds modified files -
Processing:
createListOfInputFileItems()creates list of ALL scheduled files-
Loops over entire list in
callXref()[line 314] -
Each file processed via
oneWholeFileProcessing() -
Sets
inputFileNamefor each file -
Uses
currentFileNumber(different global!) instead ofrequestFileNumber
-
-
Loop: Single invocation processes all files
LSP Mode - Single File Per Request
-
No scheduling: Takes fileName as direct parameter
-
No global state:
parseToCreateReferences(fileName)- clean interface -
Processing: Direct call, no file table lookup needed
-
Modern design: Avoids the legacy scheduling/global state complexity
8.15.7. Target: Unified Server Flow (ADR 22)
The current architecture has two initialization paths (initializeProjectContext for
OP_ACTIVE_PROJECT, initializeFileProcessing for legacy per-file) and relies on the
disk database as the source of truth for project structure. The target design unifies
these into a single path where the in-memory database is authoritative.
server() loop:
│
FOR EACH REQUEST:
│
├─ 1. IF NOT initialized:
│ ├─ Find project (.c-xrefrc), read options, discover compiler
│ │ → loadProjectSettings(): options + compiler interrogation
│ │ → Provides include paths (options.includeDirs)
│ │
│ ├─ Load disk db into memory
│ │ → loadFileNumbersFromStore(): CU entries + lastParsedMtime
│ │ → Cache/optimization, not source of truth
│ │
│ └─ projectContextInitialized = true
│
├─ 2. Config-change-aware scan (re-runs when .c-xrefrc changes)
│ ├─ IF config changed: reloadProjectConfig()
│ │ → re-reads .c-xrefrc, updates options.includeDirs + savedOptions
│ └─ IF !scanDone OR config changed:
│ → scanProjectForFilesAndIncludes(): glob CUs (.c, .y),
│ text-scan #include lines, resolve paths transitively
│ (CU dir + options.includeDirs), populate file table +
│ TypeCppInclude refs
│ → markMissingFilesAsDeleted(): CUs only (glob-discoverable)
│ → scanDone = true
│
├─ 3. Update what changed (same two-pass as ADR 20)
│ ├─ Pass 1: reparse stale CUs
│ └─ Pass 2: reparse CUs that include stale headers
│
├─ 4. Execute operation
│
└─ 5. Repeat from 2Key principles:
-
"Cold start" is not a separate path. Same code, different amount of work. With disk db: most CUs are fresh, few need reparsing. Without disk db: all CUs are unknown, all get parsed.
-
Include structure and symbol references are separate layers. Include structure is cheap (text scanning for
#include). Symbol references are expensive (full parsing). The lightweight scan provides the first; full parsing adds the second incrementally, on demand. -
Conditional includes are conservative. Text scanning sees all
#includelines regardless of#ifdefguards — a superset of the true include graph. This matches the multi-pass philosophy and is correct: a false include edge only causes one extra reparse on staleness.
This design eliminates the need for -create (replaced by the scan) and for
callXref() before refactoring (replaced by scan + incremental reparse of stale files).
It also makes the server viable for LSP, where blocking on a full project parse at
startup is not acceptable.
8.15.8. Opportunities for Alignment
The Server and Xref paths do similar things but with different names and structures, creating cognitive overhead. Potential improvements:
-
Naming consistency:
processFile()(server) vsoneWholeFileProcessing()(xref) could both use consistent naming -
Eliminate duplication: Fix the double
initInput()call in xref path -
Extract common logic: The inner "process one file" logic should be identical between modes
-
Make differences explicit:
-
Server:
for (each request) { process one file } -
Xref:
for (each scheduled file) { process one file }
-
The paths are intertwined but different, making it hard to keep in your head which one you’re modifying. Making them more similar where possible would reduce cognitive load during refactoring work.
8.16. Parsers
See the Parsing component in the Components chapter.
8.17. Integrated Preprocessor
See the Parsing component’s Internal Structure section in the Components chapter.
8.18. Refactoring and the parsers
Some refactorings need more detailed information about the code, maybe all do?
One example, at least, is parameter manipulation. Then the refactorer
calls the appropriate parser (serverEditParseBuffer()) which
collects information in the corresponding semantic actions. This
information is stored in various global variables, like
parameterBeginPosition.
The parser is filling out a ParsedInfo structure which conveys information that can be used e.g. when extracting functions etc.
| At this point I don’t understand exactly how this interaction is performed, there seems to be no way to parse only appropriate parts, so the whole file need to be re-parsed. |
Findings:
-
some global variables are set as a result of command line and arguments parsing, depending on which "command" the server is acting on
-
the semantic rules in the parser(s) contains code that matches these global variables and then inserts special lexems in the lexem stream
One example is how a Java 'move static method' was performed. It
requires a target position. That position is transferred from command
line options to global variables. When the Java parser was parsing a
class or similar it (or rather the lexer) looks at that "ddtarget
position information" and inserts a OL_MARKER_TOKEN in the stream.
| TODO: What extra "operation" the parsing should perform and return data for should be packaged into some type of "command" or parameter object that should be passed to the parser, rather than relying on global variables. |
8.19. Reading Files
Here are some speculations about how the complex file reading is structured.
Each file is identified by a filenumber, which is an index into the
file table, and seems to have a lexBuffer tied to it so that you can
just continue from where ever you were. That in turn contains a
CharacterBuffer that handles the actual character reading.
And there is also an "editorBuffer"…
The intricate interactions between these are hard to follow as the code here are littered with short character names which are copies of fields in the structures, and infested with many macros, probably in an ignorant attempt at optimizing. ("The root of all evil is premature optimization" and "Make it work, make it right, make it fast".)
It seems that everything start in initInput() in yylex.c where the
only existing call to fillFileDescriptor() is made. But you might
wonder why this function does some initial reading, this should be
pushed down to the buffers in the file descriptor.
8.19.1. Lexing/scanning
Lexing/scanning is performed in two layers, one in lexer.c which
seems to be doing the actual lexing into lexems which are put in a
lexembuffer. This contains a sequence of encoded and compressed
symbols which first has a LexemCode which is followed by extra data,
like Position. These seems to always be added but not always necessary.
The higher level "scanning" is performed, as per ususal,
by yylex.c. lexembuffer defines some functions to put and get
lexems, chars (identifiers and file names?) as well as integers and
positions.
At this point the put/get lexem functions take a pointer to a pointer to chars (which presumably is the lexem stream in the lexembuffer) which it also advances. This requires the caller to manage the LexemBuffer’s internal pointers outside and finally set them right when done.
It would be much better to call the "putLexem()"-functions with a
lexemBuffer but there seems to be a few cases where the destination
(often dd) is not a lexem stream inside a lexemBuffer. These might
be related to macro handling.
| This is a work-in-progress. Currently most of the "normal" usages are prepared to use the LexemBuffer’s pointers. But the handling of macros and defines are cases where the lexems are not put in a LexemBuffer. See the TODO.org for current status of this Mikado sequence. |
8.19.2. Semantic information
As the refactoring functions need some amount of semantic information,
in the sense of information gathered during parsing, this information
is collected in various ways when c-xref calls the "sub-task" to do
the parsing required.
Two structures hold information about various things, among which are
the memory index at certain points of the parsing. Thus it is possible
to verify e.g. that a editor region does not cover a break in block or
function structure. This structure is, at the point of writing, called
parsedInfo and definitely need to be tidied up.
8.20. Reference Database
See the Cxref component (in-memory reference tables and symbol resolution) and the Cxfile component (on-disk database format and reading) in the Components chapter.
The architectural direction for cxfile.c is documented in Chapter 17: Incremental cxfile.c Cleanup. The high-level "Memory as Truth" vision is in Chapter 15: Roadmap.
|
8.21. Editor Plugin
The editor plugin has three different responsibilities:
-
serve as the UI for the user when interacting with certain
c-xrefrelated functions -
query
c-xref serverfor symbol references and support navigating these in the source -
initiate source code operations ("refactorings") and execute the resulting edits
Basically Emacs (and probably other editors) starts c-xref in
"server-mode" using -server which connects the editor
with c-xref through stdout/stdin. If you have (setq
c-xref-debug-mode t) this command is logged in the *Messages* buffer
with the prefix "calling:".
Commands are sent from the editor to the server on its standard input.
They looks very much like normal command line options, and in fact
c-xref will parse that input in the same way using the same
code. When the editor sends an end-of-options line, the server will
start executing whatever was sent, and return some information in the
file given as an -o option when the editor starts the c-xref
server process. The file is named and created by the editor and
usually resides in /tmp. With c-xref-debug-mode set to on this is
logged as "sending:". If you (setq c-xref-debug-preserve-tmp-files
t) Emacs will also not delete the temporary files it creates so that
you can inspect them afterwards.
When the server has finished processing the command and placed the
output in the output file it sends a <sync> reply.
The editor can then pick up the result from the output file and do what it needs to do with it ("dispatching:").
8.21.1. Invocations
The editor invokes a new c-xref process for the following cases:
-
Refactoring
Each refactoring operation calls a new instance of
c-xref? -
Create Project
When a
c-xreffunction is executed in the editor and there is no project covering that file, an interactive "create project" session is started, which is run by a separatec-xrefprocess.
8.21.2. Buffers
There is some magical editor buffer management happening inside of
c-xref which is not clear to me at this point. Basically it looks
like the editor-side tries to keep the server in sync with which
buffers are opened with what file…
At this point I suspect that -preload <file1> <file2> means that the
editor has saved a copy of <file1> in <file2> and requests the server
to set up a "buffer" describing that file and use it instead of the
<file1> that recides on disk.
This is essential when doing refactoring since the version of the file
most likely only exists in the editor, so the editor has to tell the
server the current content somehow, this is the -preload option.
8.22. Editor Server
When serving an editor the c-xrefactory application is divided into
the server, c-xref and the editor part, at this point only Emacs:en
are supported so that’s implemented in the
editor/Emacs-packages.
8.22.1. Interaction
The initial invocation of the edit server creates a process with which communication is over stdin/stdout using a protocol which from the editor is basically a version of the command line options.
When the editor has delivered all information to the server it sends
'end-of-option' as a command and the edit server processes whatever it
has and responds with <sync> which means that the editor can fetch
the result in the file it named as the output file using the '-o'
option.
| As long as the communication between the editor and the server is open, the same output file will be used. This makes it hard to catch some interactions, since an editor operation might result in multiple interactions, and the output file is then re-used. |
Setting the emacs variable c-xref-debug-mode forces the editor to
copy the content of such an output file to a separate temporary file
before re-using it.
For some interactions the editor starts a completely new and fresh
c-xref process, see below. And actually you can’t do refactorings
using the server, they have to be separate calls. (Yes?) I have yet to
discover why this design choice was made.
There are many things in the sources that handles refactorings
separately, such as refactoring_options, which is a separate copy of
the options structure used only when refactoring.
|
8.22.2. Protocol
Communication between the editor and the server is performed using
text through standard input/output to/from c-xref. The protocol is
defined in src/protocol.tc and must match editor/emacs/c-xrefprotocol.el.
The definition of the protocol only caters for the server→editor part, the editor→server part consists of command lines resembling the command line options and arguments, and actually is handled by the same code.
The file protocol.tc is included in protocol.h and protocol.c
which generates definitions and declarations for the elements through
using some macros.
There is a similar structure with c-xrefprotocol.elt which
includes protocol.tc to wrap the PROTOCOL_ITEMs into
defvars.
There is also some Makefile trickery that ensures that the C and elisp impementations are in sync.
One noteable detail of the protocol is that it carries strings in their native format, utf-8. This means that lengths need to indicate characters not bytes.
8.22.3. Invocation of server
The editor fires up a server and keeps talking over the established channel (elisp function 'c-xref-start-server-process'). This probably puts extra demands on the memory management in the server, since it might need to handle multiple information sets and options (as read from a .cxrefrc-file) for multiple projects simultaneously over a longer period of time. (E.g. if the user enters the editor starting with one project and then continues to work on another then new project options need to be read, and new reference information be generated, read and cached.)
| TODO: Figure out and describe how this works by looking at the elisp-sources. |
FINDINGS:
-
c-xref-start-server-process in c-xref.el
-
c-xref-send-data-to-running-process in c-xref.el
-
c-xref-server-call-refactoring-task in c-xref.el
8.22.4. Communication Protocol
The editor server is started using the appropriate command line option and then it keeps the communication over stdin/stdout open.
The editor part sends command line options to the server, which looks something like (from the read_xrefs test case):
-encoding=european -olcxpush -urldirect "-preload" "<file>" "-olmark=0" "-olcursor=6" "<file>" -xrefrc ".c-xrefrc" -p "<project>" end-of-options
In this case the "-olcxpush" is the operative command which results in the following output
<goto> <position-lc line=1 col=4 len=66>CURDIR/single_int1.c</position-lc> </goto>
As we can see from this interaction, the server will handle (all?) input as a command line and manage the options as if it was a command line invocation.
This explains the intricate interactions between the main program and the option handling.
The reason behind this might be that a user of the editor might be editing files on multiple projects at once, so every interrogation/operation needs to clearly set the context of that operation, which is what a user would do with the command line options.
8.23. Refactoring
See the Refactory and Extract components in the Components chapter for the architecture and operation flow.
8.23.1. Refactoring Protocol Details
The refactoring protocol messages exchanged between the refactory process and the editor:
Rename Example
Invocation: -rfct-rename -renameto=NEW_NAME -olcursor=POSITION FILE
Result: A sequence of precheck/replacement pairs:
<goto>
<position-off off=POSITION len=N>FILE</position-off>
</goto>
<precheck len=N>STRING</precheck>followed by:
<goto>
<position-off off=POSITION len=N>FILE</position-off>
</goto>
<replacement>
<str len=N>ORIGINAL</str> <str len=N>REPLACEMENT</str>
</replacement>Extraction Example
Extraction (-rfct-extract-function) returns an <extraction-dialog> with three <str> parts: the call site replacement, the text to insert before the region (function header), and the text to insert after (closing brace). The editor applies these and then initiates a rename for the new function name.
Protocol Messages
<goto>{position-off}</goto>-
Move cursor to the indicated position.
<precheck len={int}>{string}</precheck>-
Verify that the text under the cursor matches the string.
<replacement>{str}{str}</replacement>-
Replace string1 under cursor with string2.
<position-off off={int} len={int}>{path}</position-off>-
Position in file ('off' is character offset).
8.24. Memory handling
c-xrefactory uses custom memory management via arena allocators rather than malloc/free for performance-critical operations.
See the Components chapter for the design and architecture of the Memory module, and the Data Structures chapter for details on the arena allocator data structure and allocation model.
For debugging memory issues, especially arena lifetime violations, see the Development Environment chapter.
8.24.1. The Memory Type
Memory allocation is managed through the Memory structure, which implements an arena/bump allocator. Different memory arenas serve different purposes:
-
cxMemory- Cross-reference database (with overflow handling) -
ppmMemory- Preprocessor macro expansion -
macroBodyMemory- Macro definition storage -
macroArgumentsMemory- Macro argument expansion -
fileTableMemory- File table entries
See Components chapter for detailed description of each arena’s purpose and lifetime.
8.24.2. Option Memory
The optMemory arena requires special handling because Options structures are copied during operation. When copying, all pointers into option memory must be adjusted to point into the target structure’s memory area, not the source’s.
Functions like copyOptions() perform this pointer adjustment through careful memory arithmetic, traversing a linked list of all memory locations that need updating.
| The linked list nodes themselves are allocated in the Options structure’s dynamic memory. |
8.25. Configuration
The legacy c-xref normally, in "production", uses a common configuration file in the
users home directory, .c-xrefrc. When a new project is defined its options will be
stored in this file as a new section.
It is possible to point to a specific configuration file using the command line option
-xrefrc which is used extensively in the tests to isolate them from the users
configuration.
Each "project" or "section" requires a name of the "project", which is the argument to
the -p command line option. And it may contain most other command line options on one
line each. These are always read, unless -no-stdop is used, before anything else. This
allows for different "default" options for each project.
8.25.1. Options
There are three possible sources for options.
-
Configuration files (~/.c-xrefrc)
-
Command line options at invocation, including server
-
Piped options sent to the server in commands
Not all options are relevant in all cases.
All options sources uses exactly the same format so that the same code for decoding them can be used.
8.25.2. Logic
When the editor has a file open it needs to "belong" to a project. The logic for finding which is very intricate and complicated.
In this code there is also checks for things like if the file is already in the index, if the configuration file has changed since last time, indicating there are scenarios that are more complicated (the server, obviously).
But I also think this code should be simplified a lot.
9. Data Structures
There are a lot of different data structures used in c-xrefactory.
This is a first step towards visualising some of them.
9.1. ReferenceableItem and Reference: Core Domain Concepts
These are the fundamental cross-reference data structures that represent the "what" and "where" of code entities.
9.1.1. ReferenceableItem
A ReferenceableItem represents a referenceable entity in the codebase - something that can be referenced from multiple locations:
-
Functions and variables
-
Types (structs, unions, enums, typedefs)
-
Macros
-
Include directives (special case:
TypeCppInclude) -
Yacc non-terminals and rules
Each ReferenceableItem contains:
-
linkName- Fully qualified name (e.g.,"MyClass::method") -
type- What kind of entity (function, variable, type, etc.) -
storage,scope,visibility- Language properties -
includeFile- ForTypeCppIncludeitems, which file is being included -
references- Linked list of allReference(occurrences) of this entity
ReferenceableItems are stored in the referenceableItemTable (hash table) and persisted to .cx files.
9.1.2. Reference (Occurrence)
A Reference represents a single occurrence of a ReferenceableItem at a specific location:
-
position- File, line, and column where this occurrence appears -
usage- How it’s used (definition, declaration, usage, etc.) -
next- Pointer to next occurrence in the list
Each ReferenceableItem maintains a linked list of all its References, allowing you to find every place that entity appears in the codebase.
Note: The term "Reference" in this context means "occurrence" - one specific use of an entity at one location. This is distinct from C++ references or reference semantics.
9.2. Symbol (Parser Symbol Table)
There is also a structure called Symbol. This is separate from ReferenceableItem and serves a different purpose:
Symbol - Parser-level symbol table entry (temporary, exists only during parsing):
-
Used by the C/Yacc parser for semantic analysis
-
Contains type information, position, storage class
-
Lives in
symbolTable(hash table) during file parsing -
Not persisted - discarded after parsing completes
ReferenceableItem - Cross-reference entity (persistent across entire codebase):
-
Created FROM Symbol properties when a referenceable construct is found
-
Stored in
referenceableItemTableand saved to.cxfiles -
Accumulates References from all files in the project
Relationship: During parsing, when the parser encounters a referenceable symbol (function, variable, etc.), it:
-
Creates a
SymbolinsymbolTablefor semantic analysis -
Creates or finds a
ReferenceableItemby copying Symbol properties -
Adds a
Referenceto that ReferenceableItem’s list -
Discards the Symbol when parsing completes
This separation allows the parser to maintain its own temporary symbol table while building the persistent cross-reference database.
9.3. Files and Buffers
Many strange things are going on with reading files so that is not completely understood yet.
Here is an initial attempt at illustrating how some of the file and text/lexem buffers are related.
It would be nice if the LexemStream structure could point to a
LexemBuffer instead of holding separate pointers which are
impossible to know what they actually point to…
|
| This could be achieved if we could remove the CharacterBuffer from LexemBuffer and make that a reference instead of a composition. Then we’d need to add a CharacterBuffer to the structures that has a LexemBuffer as a component (if they use it). |
9.4. Modes
c-xrefactory operates in different modes ("regimes" in original
c-xref parlance):
-
xref - batch mode reference generation
-
server - editor server
-
refactory - refactory browser
The default mode is "xref". The command line options -server and -refactory
selects one of the other modes. Branching is done in the final lines in
main().
The code for the modes are intertwined, probably through re-use of already existing functionality when extending to a refactoring browser.
One evidence for this is that the refactory module calls the "main task" as a "sub-task". This forces some intricate fiddling with the options data structure, like copying it. Which I don’t fully understand yet.
TODO?: Strip away the various "regimes" into more separated concerns and handle options differently.
9.5. Options
The Options datastructure is used to collect options from the
command line as well as from options/configuration files and piped
options from the editor client using process-to-process
communication.
It consists of a collection of fields of the types
-
elementary types (bool, int, …)
-
string (pointers to strings)
-
lists of strings (linked lists of pointers to strings)
9.5.1. Allocation & Copying
Options has its own allocation using optAlloc which allocates in a
separate area, currently part of the options structure and utilizing
"dynamic allocation" (dm_ functions on the Memory structure).
The Options structure are copied multiple times during a session, both
as a backup (savedOptions) and into a separate options structure
used by the Refactorer (refactoringOptions).
Since the options memory is then also copied, all pointers into the options memory need to be updated. To be able to do this, the options structure contains lists of addresses that needs to by "shifted".
When an option with a string or string list value is modified the option is registered in either the list of string valued options or the list of string list valued options. When an options structure is copied it must be performed using a deep copy function which "shifts" those options and their values (areas in the options memory) in the copy so that they point into the memory area of the copy, not the original.
After the deep copy the following point into the option memory of the copy
-
the lists of string and string list valued options (option fields)
-
all string and string valued option fields that are used (allocated)
-
all list nodes for the used option (allocated)
-
all list nodes for the string lists (allocated)
9.6. Arena Allocators (Memory)
Arena allocators (also called region-based or bump allocators) are the fundamental memory management strategy used throughout c-xrefactory for performance-critical operations like macro expansion and lexical analysis.
9.6.1. The Memory Structure
typedef struct memory {
char *name; // Arena name for diagnostics
bool (*overflowHandler)(int n); // Optional resize handler
int index; // Next allocation offset (bump pointer)
int max; // High-water mark
size_t size; // Total arena size
char *area; // Actual memory region
} Memory;9.6.2. Allocation Model
Arena allocators use bump pointer allocation:
-
Allocation: Return
&area[index], thenindex += size -
Deallocation: Bulk rollback via
FreeUntil(marker) -
Reallocation: Only possible for most recent allocation
This is extremely fast (O(1) allocation) but requires stack-like discipline for deallocation.
9.6.3. Stack-Like Discipline
Arenas follow LIFO (last-in-first-out) cleanup:
marker = ppmAllocc(0); // Save current index
temp1 = ppmAllocc(100); // Allocate
temp2 = ppmAllocc(200); // Allocate
// Use temp1, temp2...
ppmFreeUntil(marker); // Free both temp1 and temp29.6.4. Key Constraint: Top-of-Stack Reallocation
Only the most recent allocation can be resized:
buffer = ppmAllocc(1000); // Allocate buffer
temp = ppmAllocc(500); // Allocate temporary
ppmReallocc(buffer, ...); // ❌ FAILS - buffer not at topThis constraint is enforced by guards in memory.c (see Development Environment chapter).
9.6.5. Memory Arena Types
c-xrefactory uses specialized arenas for different purposes (see Components chapter for details):
-
cxMemory- Cross-reference database and symbol tables -
ppmMemory- Preprocessor macro expansion (temporary) -
macroBodyMemory- Macro body buffers -
macroArgumentsMemory- Macro argument expansion -
fileTableMemory- File table entries -
optMemory- Option strings (with special pointer adjustment)
9.7. Preload Mechanism
The preload mechanism allows the server to work with editor buffer contents that haven’t been saved to disk. This is essential for providing real-time symbol navigation and completion while the user is actively editing.
9.7.1. How It Works
When an editor buffer is modified but not yet saved:
-
Editor Action: The Emacs client writes the current buffer content to a temporary file
-
Server Request: The client sends a request with
-preload <filename> <tmpfile>options -
Buffer Association: The server creates an
EditorBufferstructure linking the on-disk filename to the temporary file containing the actual content -
Transparent Parsing: When the server needs to parse the file, it transparently reads from the temporary file instead of the on-disk file
9.7.2. Why It’s Needed
Without preload, the server would only see the last saved version of the file. The preload mechanism ensures that:
-
Symbol navigation works with the current buffer state
-
Completion suggests symbols based on what’s actually typed
-
Refactorings operate on the current code, not stale saved content
-
Users get immediate feedback without having to save constantly
9.7.3. Reference Management
When a file is preloaded, the server must handle reference updates carefully:
-
Old references from the previous file version must be removed from the reference table before parsing
-
This prevents duplicate references (one set at old positions, another at new positions)
-
The removal happens in
removeReferencesForFile()when preloaded content is detected
9.8. Browser Stack
The browser stack maintains navigation history for symbol references, allowing users to browse through code by pushing symbol lookups and navigating back through previous queries.
9.8.1. Structure
The browser stack is a linked list of OlcxReferences entries, where each entry represents a symbol lookup session:
-
Stack entries contain complete symbol information and reference lists for one navigation session
-
Top pointer indicates the current active entry being navigated
-
Root pointer tracks the base of the stack (most recent entry still available)
-
Entries between root and top are "future" navigation states that can be returned to via "next"
9.8.2. Lifecycle
-
Push: When user requests symbol references (e.g.,
-olcxpush), a new empty entry is created on the stack -
Population: After parsing, the entry is filled with
BrowsingMenustructures containing references -
Navigation: Commands like
-olcxnextand-olcxpreviousmove through references in the current entry -
Pop: User can pop back to previous entries to return to earlier symbol lookups
9.8.3. Relationship to Parsing
The browser stack is populated in two stages:
-
Parse-time: References are collected in the referenceableItemTable during file parsing
-
Menu Creation: ReferenceableItems are wrapped in BrowsingMenu structures and added to the browser stack entry via
putOnLineLoadedReferences()
This separation means that browser stack entries can become stale if files are reparsed (e.g., with preloaded content) without refreshing the stack. Users typically need to pop and re-push to get fresh reference lists after edits.
9.9. Browser Menu
A browser menu is a navigable list of referenceable items with their occurrences, organized for presentation to the user in Emacs. Multiple items may appear in a single menu when name resolution finds several candidates (e.g., symbols with the same name in different scopes).
9.9.1. BrowsingMenu Structure
Each BrowsingMenu entry is a menu item wrapping a ReferenceableItem with UI presentation state:
-
referenceable: The embedded
ReferenceableItem(the entity being browsed)-
Contains
linkName,type,storage,scope,visibility -
Contains the list of
references(occurrences) for this item
-
-
selected: Whether this item is currently selected for operations
-
visible: Whether this item passes current visibility filters
-
defaultPosition: The "best" occurrence to jump to (usually the definition)
-
defaultUsage: The usage type of the default occurrence
-
outOnLine: Display line number in the Emacs menu
-
markers: Editor markers for refactoring operations
-
next: Pointer to next menu item in the list
Key insight: BrowsingMenu is not just a menu - it’s a menu item. A collection of BrowserMenu items forms the actual menu shown to the user.
9.9.2. Multiple Menu Items in One Session
A single browser stack entry (OlcxReferences) can contain multiple BrowsingMenu items:
-
hkSelectedSym: Menu items that matched at the cursor position (after disambiguation)
-
symbolsMenu: Complete menu including related items (same name, similar signatures)
This allows users to:
-
See all candidates when a symbol is ambiguous
-
Navigate between related definitions (different scopes, include files)
-
Select specific items for refactoring operations
9.9.3. Menu Population
Browser menus are populated by scanning the referenceableItemTable:
-
Symbol lookup: Find all
ReferenceableItementries matching the requested symbol -
Menu item creation: Wrap each matching item in a
BrowsingMenustructure -
Reference collection: References are already in the ReferenceableItem
-
Sorting and filtering: Order items by relevance and apply visibility filters
-
Selection: Mark items that best match the cursor context (e.g., same file)
9.10. Putting It All Together: Domain Model Summary
Understanding the complete flow from parsing to browsing:
9.10.1. During Parsing (Building the Cross-Reference Database)
-
Parser creates Symbols: As the C/Yacc parser processes source code, it creates
Symbolentries insymbolTablefor semantic analysis -
ReferenceableItems are created/found: When encountering referenceable constructs (functions, variables, types, etc.):
-
Create a
ReferenceableItemfrom Symbol properties -
Check if it already exists in
referenceableItemTable -
If new, add it to the table; if exists, reuse the existing one
-
-
References are recorded: Add a
Reference(occurrence) to the ReferenceableItem’s list, recording position and usage -
Symbols are discarded: After parsing completes, the
symbolTableis cleared (Symbols are temporary) -
Database is persisted: ReferenceableItems and their References are saved to
.cxfiles
Result: A persistent database mapping each entity (ReferenceableItem) to all its occurrences (References) across the entire codebase.
9.10.2. During Browsing (Interactive Navigation)
-
User requests symbol info: User places cursor on a symbol and invokes a command (e.g., "push to symbol")
-
Symbol lookup: Server finds matching ReferenceableItem(s) in
referenceableItemTable -
BrowsingMenu creation: Each matching ReferenceableItem is wrapped in a
BrowserMenustructure-
Adds UI state (selected, visible, display position)
-
Marks best-fit match (e.g., same file as cursor)
-
-
Stack push: BrowsingMenu items are added to the browser stack (
OlcxReferencesentry) -
Display to user: Menu sent to Emacs showing all matching items and their occurrences
-
Navigation: User can browse through references, select items, invoke refactorings
Result: Interactive navigation through the cross-reference database with selection and filtering.
9.10.3. Key Relationships
Symbol (parser)
↓ (creates during parsing)
ReferenceableItem (persistent entity)
├─→ references: Reference* (list of occurrences)
└─→ stored in: referenceableItemTable
↓ (wrapped for browsing)
BrowsingMenu (UI wrapper)
└─→ stored in: OlcxReferences.symbolsMenu (browser stack)This architecture separates concerns:
-
Parser symbols - Temporary, for semantic analysis
-
Cross-reference database - Persistent, for finding all uses
-
Browser menus - Presentation layer, for user interaction
10. Algorithms
The code does not always explain the algorithms that it implements. This chapter will ultimately be a description of various algorithms used by c-xrefactory.
10.1. How is an Extract refactoring performed?
The region (mark and point/cursor positions) is sent to the c-xref
server in a -refactory -rfct-extract command.
The server parses the relevant file and sets some information that can be used in some prechecks that are then performed, such as structure check, and then the server answers with
<extraction-dialog>
<str .... /str>
<str .... /str>
<str .... /str>
</extraction-dialog>The first string is the code that will replace the extracted code, such as a call to the extracted function. The second string is the header part that will preceed the extracted code ("preamble"), and the third is then of course any code that needs to go after the extracted code ("postamble").
The actual code in the region is never sent to, or returned from, the server. This is handled completely by the editor extension, and used verbatim (except if it is a macro that is extracted, in which case each line is terminated by the backslash) so no changes to that code can be made.
The pre- and post-ambles might be of varying complexity. E.g. when extracting a macro, the postamble can be completely empty. When extracting a function both may contain code to transfer and restore parameters into local variables to propagate in/out variables as required.
-
The editor then requests a name from the user that it will use in a rename operation that renames the default named function/macro/variable.
Two-Phase Architecture
Extraction operates in two phases:
-
Collection Phase (during parsing): Parser semantic hooks track control flow by registering synthetic labels and collecting references within the marked region.
-
Analysis Phase (after parsing): The extraction module analyzes the collected control flow data, classifies variables by usage patterns, and generates the refactored code (call site, function definition, postamble).
This separation keeps the parser clean and makes extraction logic independently testable.
10.2. How does lexem stream management work?
Lexical analysis uses a stack of LexemStream structures to handle nested macro expansions. The key insight is that the stream type acts as a discriminator for buffer ownership and cleanup strategy.
10.2.1. The Stream Types
typedef enum {
NORMAL_STREAM, // File or local buffer
MACRO_STREAM, // Macro expansion
MACRO_ARGUMENT_STREAM, // Macro argument expansion
} LexemStreamType;
Historically, there was also a CACHED_STREAM type when the caching mechanism was still active. This confirms that stream types are fundamentally about buffer ownership and refill strategy - each type encodes where the buffer came from and how to handle it when exhausted.
|
- NORMAL_STREAM
-
Buffer from file’s
lexemBufferor a local temporary. Not allocated from arena memory, so no cleanup needed when stream exhausted. - MACRO_STREAM
-
Buffer allocated from
macroBodyMemoryarena during macro expansion. Must callmbmFreeUntil(stream.begin)when popping from stack to free the arena allocation. - MACRO_ARGUMENT_STREAM
-
Buffer allocated from
ppmMemoryarena during macro argument expansion. SignalsEND_OF_MACRO_ARGUMENT_EXCEPTIONwhen exhausted (cleanup handled by caller).
10.2.2. The Refill Algorithm
When currentInput runs out of lexems (read >= write), refillInputIfEmpty() uses the stream type to decide what to do:
while (currentInput.read >= currentInput.write) {
LexemStreamType inputType = currentInput.streamType;
if (insideMacro()) { // Stack not empty
if (inputType == MACRO_ARGUMENT_STREAM) {
return END_OF_MACRO_ARGUMENT_EXCEPTION;
}
// Only free MACRO_STREAM buffers (allocated from macroBodyMemory)
if (inputType == MACRO_STREAM) {
mbmFreeUntil(currentInput.begin);
}
currentInput = macroInputStack[--macroStackIndex]; // Pop
}
else if (inputType == NORMAL_STREAM) {
// Refill from file
buildLexemFromCharacters(¤tFile.characterBuffer, ...);
}
}10.2.3. Key Invariant
Stream type must match buffer allocation:
-
MACRO_STREAM→ buffer allocated frommacroBodyMemory -
NORMAL_STREAM→ buffer NOT from macro arenas -
MACRO_ARGUMENT_STREAM→ buffer fromppmMemory
Violating this invariant causes fatal errors when trying to free buffers from the wrong arena.
10.2.4. Common Bug Pattern
Pushing a NORMAL_STREAM onto the macro stack, then trying to free it as if it were MACRO_STREAM:
// WRONG: Blindly freeing without checking type
mbmFreeUntil(currentInput.begin); // Fails if currentInput is NORMAL_STREAM!
// CORRECT: Check type first
if (inputType == MACRO_STREAM) {
mbmFreeUntil(currentInput.begin);
}10.3. Editor Buffers and Incremental Updates
This section describes how c-xrefactory handles the reality that source code exists in
two places: on disk as files, and in memory as editor buffers. It also explains the
different update strategies and how references flow through the system.
10.3.1. Editor Buffer Abstraction
The Duality of Source Code
When a user edits code in Emacs, the source code exists in two forms:
-
Disk files: The saved state on the filesystem
-
Editor buffers: The current (possibly unsaved) state in the editor
For code analysis to be useful during active editing, c-xrefactory must treat editor buffers as the source of truth when they exist.
The Preloading Mechanism
When the Emacs client sends a command to the c-xref server (like PUSH or NEXT), it uses
the -preload option to transmit modified buffers:
-preload <original-file> <temp-file>
For example:
-olcxnext -olcursor=5 /project/foo.c -preload /project/foo.c /tmp/emacs-xxx.tmp
The process:
-
Emacs creates a temporary file containing the current buffer content
-
The temp file’s modification time represents when the buffer was last modified
-
The server loads this into an
EditorBufferstructure -
When parsing, the server reads from the temp file (buffer content) instead of the disk file
This ensures that the server analyzes what the user sees in the editor, not the potentially stale disk file.
EditorBuffer Lifecycle
EditorBuffer {
char *name; // Original filename
char *preLoadedFromFile; // Path to temp file with buffer content
time_t modificationTime; // When buffer was last modified
...
}-
Created by
loadAllOpenedEditorBuffers()at the start of each server operation -
Lives only for the duration of that operation
-
Destroyed by
closeAllEditorBuffers()at operation end
10.3.2. Modification Time Tracking
To implement incremental updates, c-xrefactory tracks when each file/buffer was last parsed.
The Fields
Each FileItem in the file table has:
-
lastParsedMtime- The modification time when we last parsed this file (any update mode) -
lastFullUpdateMtime- The modification time when we last did a FULL update (including header propagation)
These are time_t values (seconds since epoch).
Dual Semantics
The lastParsedMtime field has dual semantics depending on context:
-
For disk files: Stores the file’s mtime when it was parsed
-
For editor buffers: Stores the buffer’s mtime (from the preloaded temp file)
This works because editorFileModificationTime() abstracts over both:
time_t editorFileModificationTime(char *filename) {
EditorBuffer *buffer = getEditorBuffer(filename);
if (buffer != NULL && buffer->preLoadedFromFile != NULL) {
return buffer->modificationTime; // Buffer time
} else {
return fileModificationTime(filename); // Disk time
}
}The abstraction is seamless: code can check "has this file changed?" without caring whether it’s a disk file or editor buffer.
Change Detection
To determine if a file/buffer needs reparsing:
if (editorFileModificationTime(fileItem->name) != fileItem->lastParsedMtime) {
// File/buffer has changed since we last parsed it
reparse(fileItem);
fileItem->lastParsedMtime = editorFileModificationTime(fileItem->name);
}This pattern appears in:
-
schedulingToUpdate()- Marks files needing update before batch processing -
processModifiedFilesForNavigation()- Detects modified buffers during navigation
10.3.3. Update Strategies
C-xrefactory has two update strategies that trade off speed against completeness.
Fast Update (Default)
When used:
-
Automatic updates before PUSH operations (if enabled)
-
Explicit
-fastupdatecommand
What it does:
-
Checks which source files (.c) have changed (compares modification times)
-
Reparses only those changed source files
-
Updates the references database
Trade-off:
-
✅ Fast: Only reparses files that actually changed
-
❌ Incomplete: Doesn’t detect when header files change
Example:
foo.h modified → fast update → foo.h not reparsed foo.c unchanged → foo.c not reparsed Result: foo.c still has stale information about symbols from foo.h
Full Update
When used:
-
Explicit
-updatecommand -
When
-exactpositionresolveis enabled (forces full update)
What it does:
-
Checks which files (source OR headers) have changed
-
If a header changed, finds all source files that include it (transitively)
-
Reparses all affected source files
-
Updates the references database
The algorithm (makeIncludeClosureOfFilesToUpdate):
-
Mark all changed files as
scheduledToUpdate -
For each marked file:
-
Find all files that
#includeit (by looking up include references) -
Mark those files as
scheduledToUpdatetoo
-
-
Repeat until no new files are added (transitive closure)
-
Reparse all marked source files
Trade-off:
-
✅ Complete: Catches header changes and propagates to all users
-
❌ Slower: Can trigger reparsing of many source files if a common header changes
Example:
common.h modified → full update → finds 50 files that include it Result: Reparses all 50 source files to pick up header changes
When Does the Difference Matter?
With modern CPUs and SSDs, the performance difference is often negligible for small to medium projects. The fast update’s header-blindness can lead to subtle bugs where changes don’t propagate. Full update is generally safer and more correct.
10.3.4. Reference Lifecycle
References flow through multiple stages in c-xrefactory, with different storage locations and ownership models at each stage.
Stage 1: Parsing
When a file is parsed:
-
Symbols are discovered (functions, variables, types, etc.)
-
For each symbol, a
ReferenceableItemis created or looked up in thereferenceableItemTable -
Each usage of that symbol creates a
Referencewith a position -
The reference is added to the referenceable’s reference list
Storage: cxMemory (a custom arena allocator)
Lifetime: Lives until the next update that reparses that file
Stage 2: The ReferenceableItemTable
The canonical storage for all references.
ReferenceableItem {
char *linkName; // Symbol identifier
Type type; // Function, variable, macro, etc.
Reference *references; // Linked list of all uses
...
}Key properties:
-
Allocated in
cxMemory -
Persistent across multiple server operations
-
Updated incrementally as files are reparsed
-
References are not individually free’d - they’re arena-allocated
Stage 3: Session Stacks
When a user performs a PUSH operation (browsing a symbol), a session is created:
SessionStackEntry {
BrowsingMenu *menu; // Selected symbols
Reference *references; // COPY of references for navigation
Reference *current; // Current position in navigation
...
}Key properties:
-
The
referenceslist is a copy (viamalloc) of references from the referenceableItemTable -
Each reference is individually allocated with
malloc(seeaddReferenceToList) -
When the session is destroyed, references are individually
free’d (see `freeReferences) -
Sessions are snapshots in time - they don’t automatically update when the table changes
Why Separate Storage?
Memory ownership:
-
Table references: Arena-allocated, freed in bulk
-
Session references: Individually allocated, individually freed
If sessions pointed directly to table references, we’d have:
-
Dangling pointers when the table is updated
-
Double-free errors when sessions are destroyed
-
Memory corruption from mixed allocation strategies
Snapshots vs. live data:
-
The table is the "live" source of truth
-
Sessions are working copies for a specific browsing operation
-
Users expect their navigation stack to be stable during browsing
The Staleness Problem
The separation causes a problem: session references can become stale.
Scenario:
-
User PUSHes symbol
foo→ Session created with references at lines 10, 50, 100 -
User edits a file, adding lines
-
User navigates with NEXT → Session still points to lines 10, 50, 100 (wrong!)
Solution: processModifiedFilesForNavigation()
When NEXT/PREVIOUS operations occur, the server:
-
Detects which editor buffers have changed (modification time check)
-
Reparses those buffers (updates referenceableItemTable)
-
Rebuilds the current session’s reference list from the updated table
-
Preserves the user’s navigation position by index
// Find user's position in old list
int currentIndex = 0;
Reference *ref = session->references;
while (ref != NULL && ref != session->current) {
currentIndex++;
ref = ref->next;
}
// Free old list and rebuild from table
freeReferences(session->references);
session->references = NULL;
for (BrowsingMenu *menu = session->menu; menu != NULL; menu = menu->next) {
if (menu->selected) {
ReferenceableItem *updatedItem = lookupInTable(&menu->referenceable);
addReferencesFromFileToList(updatedItem->references, ANY_FILE,
&session->references);
}
}
// Restore position by index
ref = session->references;
for (int i = 0; i < currentIndex && ref->next != NULL; i++) {
ref = ref->next;
}
session->current = ref;This keeps navigation working correctly with live-edited code.
Trade-offs of the Incremental Approach
Advantages:
-
Minimal latency - only reparses changed buffers
-
Uses editor buffer content (user’s current view)
-
Preserves navigation position naturally
Limitations:
-
Like fast update: doesn’t reparse includers of changed headers
-
Only updates the current session (other sessions on the stack remain stale)
-
Only happens during NEXT/PREVIOUS (not other operations)
For typical usage (navigating within files being actively edited), these limitations rarely matter. A fresh PUSH creates a new session with fresh references.
10.3.5. Summary
The key insights:
-
Editor buffers are the source of truth when they exist (via preloading)
-
Modification times are tracked uniformly for files and buffers
-
Fast update trades completeness for speed (doesn’t chase headers)
-
Full update is more thorough but can reparse many files
-
References live in two places: canonical table (arena memory) and session copies (malloc)
-
Sessions are snapshots that can become stale, requiring incremental rebuilding during navigation
10.4. How does …
TBD.
11. Development Environment
11.1. Developing, here be dragons…
First the code is terrible, lots of single and double character
variables (cc, ccc, ..) and lost of administration on local
variables rather than the structures that are actually there. And
there are also a lot of macros. Unfortunately macros are hard to
refactor to functions. (But I’m making progress…)
As there is no general way to refactor a macro to a function, various techniques must be applied. I wrote a blog post about one that have been fairly successful.
But actually it’s rather fun to be able to make small changes and see the structure emerge, hone your refactoring and design skills, and working on a project that started 20 years ago which still is valuable, to me, and I hope, to others.
There should probably be a whole section on how to contribute and
develop c-xrefactory but until then here’s a short list of what
you need:
-
C development environment (GNU/Clang/Make/…)
-
Unittests are written using
Cgreen -
Clean code and refactoring knowledge (to drive the code to a better and cleaner state)
Helpful would be:
-
Compiler building knowledge (in the general sense, Yacc, but AST:s and symbol table stuff are heavily used)
11.2. Setup
TBD.
11.3. Building
You should be able build c-xref using something like (may have changed over time…)
cd src make make unit make test
But since the details of the building process are somewhat contrieved and not so easy to see through, here’s the place where that should be described.
One step in the build process was generating initialization information
for all the things in standard include files, which of course became
very dependent on the system you are running this on. This has now moved
into functions inside c-xref itself, like finding DEFINEs and include
paths.
The initial recovered c-xrefactory relied on having a working c-xref for the current system. I don’t really know how they managed to do that for all the various systems they were supporting.
Modern thinking is that you should always be able to build from source, so this is something that needed change. We also want to distribute c-xref as an el-get library which requires building from source and should generate a version specific for the current system.
The strategy selected, until some better idea comes along, is to try to build a c-xref.bs, if there isn’t one already, from the sources in the repository and then use that to re-generate the definitions and rebuild a proper c-xref. See Bootstrapping.
We have managed to remove the complete bootstrapping step, so c-xrefactory
now builds like any other project.
11.4. Versions
The current sources are in 1.6.X range. This is the same as the orginal xrefactory and probably also the proprietary C++ supporting version.
There is an option, "-xrefactory-II", that might indicate that
something was going on. But currently the only difference seems to be
if the edit server protocol output is in the form of non-structured
fprintf:s or using functions in the ppc-family (either calling
ppcGenRecord() or `fprint`ing using some PPC-symbol). This, and
hinted to in how the emacs-part starts the server and some initial
server option variables in refactory.c, indicates that the
communication from the editor and the refactory server is using
this. It does not look like this is a forward to next generation
attempt.
What we should do is investigate if this switch actually is used anywhere but in the editor server context, and if so, if it can be made the default and the 'non-xrefactory-II' communication removed.
11.5. Coding
11.5.1. Naming
C-xref started (probably) as a cross-referencer for the languages supported (C, Java, C++), orginally had the name "xref" which became "xrefactory" when refactoring support was added. And when Mariàn released a "C only" version in 2009 most of all the "xref" references and names was changed to "c-xref". So, as most software, there is a history and a naming legacy to remember.
11.5.2. Modules and Include Files
The source code for c-xrefactory was using a very old C style with a
separate proto.h where all prototypes for all externally visible
functions were placed. Definitions are all over the place and it was
hard to see where data is actually declared. This must change into
module-oriented include-strategy.
Of course this will have to change into the modern x.h/x.c externally visible interface model so that we get clean modules that can be unittested.
The function prototypes have been now moved out to header files for each "module". Some of the types have also done that, but this is still a work in progress.
11.6. Debugging
TBD. Attachning gdb, server-driver…
yaccp from src/.gdbinit can ease the printing of Yacc semantic data fields…
A helpful option is the recently added -commandlog=… which allows
you to capture all command arguments sent to the server/xref process
to a file. This makes it possible to capture command sequences and
"replay" them. Useful both for debugging and creating tests.
11.6.1. Arena Allocator Lifetime Violations
The preprocessor macro expansion code uses arena allocators (ppmMemory, macroBodyMemory)
with stack-like discipline. Arena allocators are fast (pointer bumping) but require
careful lifetime management.
The Problem Pattern
Arena allocators can only resize the most recent allocation ("top-of-stack"). A common violation occurs when trying to resize a buffer after other allocations:
buffer = ppmAllocc(size); // Allocate buffer
marker = ppmAllocc(0); // Save marker for cleanup
temp = ppmAllocc(tempSize); // Allocate temporary
ppmReallocc(buffer, newSize, ...); // ❌ FAILS - buffer not at top!
ppmFreeUntil(marker); // Free temporariesThe correct pattern frees temporaries before growing the buffer:
buffer = ppmAllocc(size); // Allocate buffer
marker = ppmAllocc(0); // Save marker
temp = ppmAllocc(tempSize); // Allocate temporary (use it)
ppmFreeUntil(marker); // Free temporaries FIRST
ppmReallocc(buffer, newSize, ...); // ✅ Works - buffer now at topLifetime Violation Guards
The arena allocator includes guards that catch lifetime violations with detailed diagnostics:
- Guard 1: Buffer Resize Guard (
memory.cinmemoryRealloc()) -
Checks buffer is at top-of-stack before resizing. Provides expected vs actual locations and suggests moving
ppmFreeUntil()earlier. - Guard 2: FreeUntil Bounds Guard (
memory.cinmemoryFreeUntil()) -
Ensures marker is within valid allocated range. Catches corrupted or wrong-arena markers.
- Guard 3: Top-of-Stack Helper (
memoryIsAtTop()) -
Allows explicit verification before operations requiring top-of-stack:
assert(memoryIsAtTop(&ppmMemory, buffer, oldSize)); ppmReallocc(buffer, newSize, sizeof(char), oldSize);
Example: test_collation_long_expansion
This test case triggered the violation guard when macro expansion created a very large
output (19 FLAG_STRING invocations). The collate() function was calling ppmFreeUntil()
after copyRemainingLexems(), which needed to grow the caller’s buffer.
The fix: move ppmFreeUntil() to before copyRemainingLexems(). By this point,
temporary allocations from macro expansion were already used and could be freed,
allowing the buffer to become top-of-stack again.
Debugging With Guards
When a guard triggers:
-
Read the fatal error messages - they explain what went wrong
-
Look for the assertion location in the stack trace
-
Check if
ppmFreeUntil()is being called too late -
Verify buffer growth happens after temporaries are freed
The guards turn subtle crashes into clear diagnostics that point to the fix.
11.7. Testing
11.7.1. Unittests
There are not very many unittests at this point, only covering a quarter of the code. The "units" in this project are unclear and entangled so creating unittests is hard since it was not build to be tested, test driven or even clearly modularized.
All unittests use Cgreen as the unittest framework. If you are unfamiliar with it the
most important point is that it can mock functions, so you will find mock
implementations of all external functions for a module in a corresponding
<module>.mock file.
Many modules are at least under test, meaning there is a <module>_tests.c in the unittest directory. Often only containing an empty test.
11.7.2. Acceptance Tests
In the tests directory you will find tests that exercise the external behaviour of
c-xref, "acceptance tests" or "system tests". Some tests actually do only that, they
wouldn’t really count as tests as there are no verification except for the code being
executed.
There are two basic strategies for the tests:
-
run a
c-xrefcommand, catch its output and verify -
run a series of command using the EDIT_SERVER_DRIVER, collect output and results and verify
Some tests do not even test its output in any meaningful way and only provide coverage.
Some tests do a very bad job at verifying, either because my understanding at that time was very low, or because it is hard to verify the output. E.g. a "test" for generating references might only grepping the CXrefs files for some strings, not verifying that they actually point to the correct place.
Hopefully this will change as the code gets into a better state and the understanding grows.
11.7.3. Test Structure
Tests live in the tests directory and are auto-discovered by name: any directory starting with test_ will be recognized as a test case.
Each test typically includes:
-
source.c(or similar) - the code under test -
expected- the expected output -
Makefile- test runner that uses the boilerplate
Most tests use tests/Makefile.boilerplate which provides common macros:
include ../Makefile.boilerplate
$(TEST):
$(COMMAND) source.c -o output.tmp
$(NORMALIZE) output.tmp > output
$(VERIFY)The key macros are:
$(COMMAND)-
Runs
c-xrefwith standard options and the test’s.c-xrefrc $(NORMALIZE)-
Removes timestamps and other variable output
$(VERIFY)-
Compares
outputwithexpected, removesoutputon success
When $(VERIFY) passes, the output file is removed. This means you can easily identify failing tests by looking for test directories that still contain an output file. The utils/failing script lists these.
To suspend a test (skip it during test runs), create a .suspended file in the test directory.
11.7.4. General Setup
Since all(?) c-xref operation rely on an options file which must
contain absolute file paths (because the server runs as a separate
process) it must be generated whenever the tests are to be run in a
different location (new clone, test was renamed, …).
This is performed by using a common template in tests and a target
in tests/Maefile.boilerplate.
Each test should have a clean target that removes any temporary and
generated files, including the .c-xrefrc file and generated
references. This way it is easy to ensure that all tests have updated
.c-xrefrc files.
11.7.5. Edit Server Driver Tests
Since many operations are performed from the editor, and the editor starts an "edit server" process, many tests need to emulate this behaviour.
The edit server session is mostly used for navigation. Refactorings
are actually performed as separate invocations of c-xref.
In utils there is a server_driver.py script, which will take as
input a file containing a sequence of commands. You can use this to
start an edit, refactory or reference server session and then feed it
with commands in the same fashion as an editor would do. The script
also handles the communication through the buffer file (see [Editor
Interface](./Design:-Editor-Interface)).
11.7.6. Creating More Edit Server Tests
You can relatively easy re-create a sequence of interactions by using the
sandboxed Emacs in tests/sandboxed_emacs.
There are two ways to use it, "make spy" or "make pure". With the "spy" an intermediate spy is injected between the editor and the edit server, capturing the interaction to a file.
With "pure" you just get the editor setup with c-xref-debug-mode and
c-xref-debug-preserve-tmp-files on. This means that you can do what
ever editor interactions you want and see the communication in the
*Messages* buffer. See [Editor Interface](./Design:-Editor-Interface)
for details.
Once you have figure out which part of the *Messages* buffer are
interesting you can copy that out to a file and run
utils/messages2commands.py on it to get a file formatted for input
to server_driver.py.
the messages2commands script converts all occurrences of the
current directory to CURDIR so it is handy to be in the same directory
as the sources when you run the conversion.
|
the messages2commands script removes any -preload so you
need to take care that the positions inside the buffers are not
changed between interactions lest the -olcursor and -olmark will
be wrong. (You can just undo the change after a refactoring or
rename). Of course this also applies if you want to mimic a sequence
of refactorings, like the jexercise move method example. Sources will
then change so the next refactoring works from content of buffers, so you
have to handle this specifically.
|
-preload is the mechanism where the editor can send modified
buffers to c-xref so thay you don’t have to save between
refactorings, which is particularly important in the case of extract
since the extraction creates a default name which the editor then does
a rename of.
|
11.8. Utilities
11.8.1. Covers
utils/covers.py is a Python script that, in some enviroments, can list which test cases execute a particular line.
This is handy when you want to debug or step through a particular part of the code.
Find a test that covers that particular line and run it using the debugger (usually make debug in the test directory).
Synopsis:
covers.py <file> <line>
11.8.2. Sandboxed
utils/sandboxed starts a sandboxed Emacs that uses the current elisp code and the c-xref from src.
This allows you to run a test changes without having to polute your own setup.
This actually runs the tests/sandboxed_emacs pure version, which also sets up a completely isolated Emacs environment with its own packages loaded, configuration etc.
See below.
Synopsis:
sandboxed
11.9. Debugging the protocol
There is a "pipe spy" in tests/sandboxed_emacs. You can build the
spy using
make spy
and then start a sandboxed Emacs which invokes the spy using
make
This Emacs will be sandboxed to use its own .emacs-files and have HOME set to this directory.
The spy will log the communication between Emacs and the real
c-xref (src/c-xref) in log files in /tmp.
NOTE that Emacs will invoke several instanced of what it believes is
the real c-xref so there will be several log files to inspect.
12. Deployment
TBD.
13. About the Decision Log
13.1. Overview
The decision log documents choices that have shaped the architecture, implementation, and direction of c-xrefactory. Most decisions from the original 1990s development are lost to history, but as they can be deduced from the codebase and commit history, they are being retroactively documented.
All architectural decisions are recorded using the Architecture Decision Record (ADR) format and stored in the adr/ directory. These ADRs are automatically integrated into the Structurizr documentation system.
13.2. Viewing Decision Records
The ADRs can be accessed in several ways:
-
Via Structurizr: When viewing the Structurizr documentation, navigate to the "Decisions" section to see all ADRs with cross-references and visualizations.
-
Directly in the repository: Browse the adr/ directory for markdown files containing individual decision records.
-
Command line: Use
ls doc/adr/*.mdfrom the project root to list all decisions.
13.3. Decision Categories
Current ADRs cover several categories:
-
Simplification decisions: Removing unused features (Java support, HTML generation, etc.)
-
Tooling decisions: Choice of ADR format, documentation system
-
Configuration decisions: Automatic config file discovery
-
Format decisions: Reference data storage format
For the complete list of decisions and their rationale, see the ADR directory or the Decisions section in the Structurizr documentation.
13.4. Creating New ADRs
When making significant architectural decisions:
-
Copy the template from
adr/templates/ -
Number it sequentially (e.g.,
0012-description.md) -
Fill in the context, decision, and consequences
-
Commit it alongside the implementation
-
Reference it in commit messages and pull requests
See ADR-0007 for details on the ADR format and process.
14. Roadmap
This chapter outlines the high-level architectural and feature goals for c-xrefactory. For implementation details, see Chapter 17: Major Codebase Improvements.
14.1. Guiding Principles
-
Incremental improvement: Each step should provide immediate value while moving toward long-term goals
-
Test-driven modernization: Maintain 85%+ test coverage to enable confident refactoring
-
Backward compatibility: Preserve existing Emacs workflows while enabling modern IDE integration
-
Architectural simplification: Replace artificial mode distinctions with unified, smart on-demand behavior
-
Legacy code respect: Work with the existing 1990s codebase thoughtfully, not against it
14.2. Architectural Vision: Memory as Truth
14.2.1. The Goal
In-memory references become the single source of truth. Currently, the system has two sources (in-memory referenceableItemTable and .cx files on disk) with different code paths for navigation vs. refactoring. This creates complexity, bugs, and makes preloaded editor buffers work inconsistently.
14.2.2. Dependency Chain
The following diagram shows how the remaining architectural pieces depend on each other. Work proceeds from bottom to top.
Memory is truth
(convergence point)
/ \
v v
No callXref in .cx becomes
refactoring startup snapshot
| |
v v
ADR 22: Lightweight Index-based sessions
file structure scan (keys + positions,
(replaces -create not copies)
and callXref) |
| |
v v
┌─────────────────────────────────────┐
│ FOUNDATION (done) │
│ - ADR-0020: Sync before dispatch │
│ - .cx loaded as startup snapshot │
│ - Client sends only dirty buffers │
│ - Single-project server (ADR-0021) │
│ - Project-local config (ADR-0005) │
│ - Unified startup (shared init) │
└─────────────────────────────────────┘
14.2.3. Component Summary
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
Separate sync from dispatch (done) |
Server-side restructuring (ADR-0020): the server entry point reparses stale files before dispatching any operation. Pass 1 reparses stale CUs, Pass 2 walks the reverse-include graph (via |
Lightweight file structure scanning |
Replace the expensive full-project |
Index-based sessions |
Session stores symbol key + current position instead of copying all references. Navigation reads directly from in-memory table, eliminating the "stale session copies" problem. Depends on upfront refresh (ADR 20) so that the table is always current when sessions read from it. |
No callXref in refactoring |
Refactoring uses same in-memory table as navigation, with lightweight scanning replacing |
Disk snapshot strategy (read side operational) |
The |
Search reads from in-memory table |
|
Snapshot write triggers |
The save mechanism exists ( All buffers saved: when no editor buffers are modified, the in-memory state is consistent with disk — a clean moment to snapshot. The snapshot must only persist disk-file-derived references (not modified-buffer data), so "all saved" is the natural condition. This is the primary trigger during normal workflow. Clean exit: the Project change: Dirty kills (crash, |
14.2.4. Incremental Implementation Path
Both navigation and refactoring already use the same in-memory ReferenceableItemTable (see Chapter 18: Unified In-Memory Table Discovery for details). The infrastructure for memory-as-truth is largely already in place:
-
Include structure is already tracked via
TypeCppIncludereferences in the reference table — the same mechanism that full parsing creates. Lightweight scanning (ADR 22) would populate these without full parsing. -
Staleness detection is already working: mtime checks on editor buffers, entry-point reparse with transitive include-graph walking (ADR 20).
-
Graduated update scope already exists:
computeUpdateOptionForSymbol()decides per-refactoring whether no update, fast update, or full update is needed based on symbol visibility and scope.
The path forward is:
-
Lightweight scanning replaces
-create— discover CUs and include structure without full parsing. Populate the sameTypeCppIncludereferences. No disk db write needed. -
Same scanning replaces
callXref()before refactoring — scan + mtime check + reparse stale files in the include closure. The graduated scope decision (computeUpdateOptionForSymbol) stays the same. -
.cxbecomes startup snapshot — loaded once at startup for fast warm start, never consulted during operation. The in-memory table is authoritative.
14.2.5. .cx File: Startup Snapshot
Once memory is truth, the .cx file is a startup snapshot — a serialized copy of previously-computed references that avoids a full project parse on server start.
Startup sequence:
-
Load snapshot from
.cx(if it exists) -
Compare each entry’s stored mtime against the current disk file
-
Re-parse any files that changed since the snapshot was written
-
Client connects, sends preloaded buffers — those are parsed into memory, overriding disk state
After startup, the .cx file is not consulted. All operations read from the in-memory table.
Writing the snapshot:
The snapshot is written from disk-file-derived references only. Modified-buffer data must never be persisted — the snapshot reflects disk state, so that startup validation (step 2) remains correct.
Cold start (no .cx file): All project source files are parsed. This is slower but self-healing — no manual action needed to recover from a missing or corrupt snapshot.
14.2.6. Related Decisions and Details
-
ADR-0005: Automatically find config files — enables project discovery by upward search
-
ADR-0013: No archaic extern patterns — limits symbol visibility to include-based, making include closure complete
-
ADR-0014: Adopt on-demand parsing architecture — formalizes this direction
-
ADR-0020: Separate sync from dispatch — implemented, entry-point reparse with include-graph walking
-
ADR-0021: Single-project server policy — foundation for index-based sessions
-
ADR-0022: Lightweight file structure scanning — replaces
-createandcallXref() -
Chapter 17: Incremental
cxfile.ccleanup,parseBufferUsingServerbridge removal
14.3. Optimization
Once the core architectural path (lightweight scan, entry refresh, memory-as-truth) is functional, targeted optimizations can reduce cold-start latency and improve responsiveness on large projects.
| Optimization | Description |
|---|---|
Header-filtered sibling parsing |
Entry refresh pass 3 currently parses all CUs sharing any header with the request file. On large projects this pulls in a large fraction of all CUs (e.g. on ffmpeg, navigating |
Extend scan to capture |
The lightweight scan currently only matches |
Lexing cache re-introduction |
The lexing cache (pre-tokenized file content) was present in the original codebase but lost during restructuring. Re-enabling it avoids repeated lexing of the same file across multiple parse passes. |
Parallel parsing |
Even with header-filtered sibling parsing, core API headers in large projects can fan out to hundreds of CUs (e.g. |
14.4. Known Limitations
The following are known consequences of the current entry refresh implementation. Each is deliberately deferred because it either has low practical impact or dissolves naturally with planned architectural changes.
| Limitation | Impact and reasoning | Dissolves with |
|---|---|---|
Re-scan doesn’t clear old include refs |
When a config change triggers a re-scan, new |
Could be fixed independently by clearing outgoing include refs per CU before re-scanning. Not urgent enough to justify the API addition. |
Double progress bar on cold start |
The lightweight scan only captures |
Extending scan to |
Pass 3 parses too many siblings |
Pass 3 parses all CUs sharing any header with the request file. On large projects with widely-shared utility headers this pulls in a large fraction of all CUs (e.g. ffmpeg |
Header-filtered sibling parsing: identify the navigated symbol’s defining header during dispatch, then parse only CUs sharing that header. Challenge: Pass 3 runs during sync (before dispatch), so this requires bridging the sync/dispatch boundary. |
Stale sessions after POP |
Sessions hold copies of references at the time the session was created. Only the top session is refreshed by entry refresh. After editing a header and navigating back (POP), the previous session may show stale positions — e.g. an old location kept in parallel with the new one. Functionally annoying but not data-corrupting. |
Index-based sessions (keys + positions instead of copies) — sessions would read directly from the in-memory table, which is always current after entry refresh. |
14.5. Feature Vision: Full LSP Support
14.5.1. The Goal
Enable VS Code, Neovim, and other LSP-capable editors to use c-xrefactory’s refactoring and navigation features with full feature parity to the Emacs integration.
14.5.2. Current State
-
Go-to-definition for functions, global variables, types (single file only)
-
Files parsed on
didOpenonly, populating the globalreferenceableItemTable -
No project initialization — no
.c-xrefrc, no compiler discovery, no disk db -
No
didChangeordidSavehandlers -
Known bug: file table size changes cause wrong positions (hash distribution)
14.5.3. Architectural Insight: LSP Document Events as Entry Refresh
The native Emacs path has a mature sync/execute separation (ADR 20): before each operation, reparse stale files in three passes, then execute with a current in-memory table. The LSP protocol provides the same separation naturally — document lifecycle events (didOpen, didChange, didSave) are sync points, and requests (definition, references) are operations that assume the table is current.
This means the LSP path does not need its own architecture. It can reuse the same initialization and reparsing infrastructure as the native path, triggered by different events.
14.5.4. Dependency Chain
Multi-file navigation
(definition, references,
rename across files)
|
v
Use referenceableItemTable
instead of separate db (done)
/ \
v v
Reparse on Project init
document events on LSP startup
(didOpen/didChange (find project,
→ parse file, load .c-xrefrc,
didSave → pass 2 compiler discovery,
includer reparse) disk db + scan)
| |
v v
┌─────────────────────────────────────┐
│ FOUNDATION (done) │
│ - parseToCreateReferences() │
│ - referenceableItemTable │
│ - Lightweight scan (ADR 22) │
│ - Entry refresh passes 1-3 │
│ - initializeProjectContext() │
│ - loadFileNumbersFromStore() │
└─────────────────────────────────────┘
14.5.5. Component Summary
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
Use |
The separate |
Project initialization on LSP startup (step 2) |
On |
Reparse on document events (step 3) |
|
Multi-file navigation (step 4) |
With steps 1-3, the |
14.5.6. Planned Capabilities
Once the foundation above is in place, the following LSP features become possible:
| Feature | Enables |
|---|---|
Multi-file navigation |
Jump to definitions in other files without opening them first |
Find all references |
Show all usages of a symbol across the project |
Hover information |
Display type and documentation on mouse hover |
Code completion |
Context-aware symbol completion |
Rename refactoring |
Safe rename across all files |
Workspace search |
Find symbols by name across project |
14.5.7. Dependencies
Steps 1-3 above are independent of the "Memory as Truth" convergence — they reuse existing infrastructure as-is. Full feature parity (rename, extract) additionally depends on:
-
Rename refactoring requires the "no callXref" path
-
All features benefit from single-project server simplicity (ADR 21)
14.6. Feature Vision: Modern Refactorings
14.6.1. The Goal
Provide refactoring capabilities that understand C semantics, going beyond what generic text-based tools can offer.
14.6.2. Current Capabilities
-
Rename (symbols, parameters, macros)
-
Extract function/macro/variable
-
Add/delete/reorder parameters
-
Move function between files (Phase 1 MVP)
14.6.3. Planned Improvements
| Feature | Value |
|---|---|
Move function Phase 2 |
Automatically add function declaration to target header file |
Move function Phase 3 |
Detect and optionally move tightly-coupled static helper functions |
Smart include management |
Automatically add/remove |
Refactoring preview |
Show what will be changed before applying |
14.6.4. Details
See Chapter 16: Move Function Between Files for implementation details and phase breakdown.
15. Planned Features
This chapter documents planned user-facing features—new refactorings, navigation capabilities, and editor integrations. These represent functionality users will interact with directly.
For internal architectural improvements and code quality work, see Chapter 17: Major Codebase Improvements.
For detailed specifications of refactoring operations (both existing and planned), see Chapter 19: Refactoring Recipes.
15.1. Move Function Between Files
Status: Phase 1 complete (December 2024)
15.1.1. Use Case
Reorganize code by moving function definitions between source files while maintaining correctness. Essential for refactoring large codebases into better module structure.
Example: Extract a utility function from main.c to utils.c, automatically handling visibility changes and header declarations.
15.1.2. What Works Now
-
Move a function from one source file to another
-
Automatically removes possible
statickeyword (makes function externally accessible) -
Adds extern declaration to target file’s header
-
Preserves comments and function decorations
-
Works for both C and Yacc files
15.1.3. Next steps
Remove extern declaration: Remove the moved functions extern declaration from the header file for the source, if the function was not static.
Include management: Automatically add necessary #include directives based on dependencies.
Helper function detection: Identify and optionally move static helper functions that the moved function depends on. Prevents broken builds.
Smarter header placement: Automatically find the right location in header files based on existing declarations and dependencies.
Preview: Show what will be changed before applying the refactoring.
15.2. LSP Integration
Status: EXPERIMENTAL (January 2026)
15.2.1. Use Case
@startuml
Bob -> Alice : hello
@endumlLanguage Server Protocol (LSP) integration enables c-xrefactory to work with modern editors and IDEs (VS Code, vim/neovim with LSP plugins, etc.) beyond Emacs. This opens c-xrefactory’s refactoring and navigation capabilities to a much wider audience.
15.2.2. What Works
Go to Definition (textDocument/definition):
-
Functions - Jump to function definition from any call site
-
Global variables - Navigate to variable declarations
-
Types - Find typedef and struct definitions
File Parsing:
-
Files are parsed as they’re opened in the editor
-
Symbols become available for navigation immediately
15.2.3. Current Limitations
Single-file scope: Only symbols in the currently opened file are accessible. To navigate to a function in another file, you must first open that file.
No local variables: Go-to-definition doesn’t work for local variables or function parameters. This works in Emacs mode but requires architectural changes for LSP.
Missing LSP features: Only textDocument/definition is implemented. Coming features:
-
Find all references
-
Hover information
-
Code completion
-
Rename refactoring
-
Organize imports
15.2.4. How to Use
See the README for LSP client configuration examples. Basic setup:
-
Build c-xrefactory with
make -
Configure your editor’s LSP client to use
c-xref -lspas the server command -
Open C or Yacc files
-
Use your editor’s "go to definition" command
15.2.5. Related Work
-
Chapter 17: Major Codebase Improvements discusses the technical architecture
-
Multi-file support requires include graph and on-demand parsing (foundational work described in Chapter 17)
15.3. Rename function handles expect
Many unittest frameworks have a feature for isolating a unit, often referred to as "mocks", in C the "unit" of mocking/stubbing/doubling is almost always a function. These mocks need to understand how they should respond to a call. As they have no logic they are "programmed" by expressing conditions and responses.
In particular, Cgreen, has an expect() which takes the function name as the first
parameter, and then constraints to apply and values to return. This is implemented using
CPP macros so the function name is just text, and cannot be detected using normal
C-parsing/analysis.
Renaming a function that appears in an expect will not rename that reference. This
will usually cause the unittest to fail, because there is no call to that, no longer
existin, function.
A handy extension of the "Rename Function" would be to find these using some special magic and replace them too.
15.4. Migrate to project local config
Previously c-xrefactory promoted a user-central config file, ~/.c-xrefrc which
contained the config for all projects by containing a section for each project. The "New
Project" wizard in the Emacs client created new sections in this file.
Since 1.9 the promoted model is a project local config file, a .c-xrefrc in the root
of the project tree. The main advantage is that it can be checked in to repo and it will
not contain absolute file paths.
Legacy project configs will continue to work, but a user might want to migrate a project. It’s fairly easy to do by hand, but as a polishing touch, providing a client operation to do that would be nice.
There is a natural trigger for this: since the Emacs client no longer sends -xrefrc and
the server’s upward search for .c-xrefrc stops before the home directory, a legacy user
with only ~/.c-xrefrc will get a "No project found" prompt. Instead of only offering
"Create new project?", the client could check ~/.c-xrefrc for a section matching the
current file, and if found, offer to migrate that section to a project-local .c-xrefrc.
15.5. Indexing Log Buffer
Status: Planned
15.5.1. Background
When the server does a cold start (no disk database), it parses all discovered compilation units to populate in-memory references. During this parsing, warnings and errors may occur (e.g., missing include files, syntax errors from missing -D defines). These are expected and harmless — c-xrefactory continues best-effort — but users benefit from seeing them to tune their .c-xrefrc (adding -I paths, -D defines, etc.).
The legacy -create command in Emacs offered "View log file?" after completion, showing a file with all parsing messages. The cold start server path needs an equivalent.
There are also other situations when a re-parse or re-discovery might throw the same kind of errors.
15.5.2. Problem
The current protocol has no non-modal message channel. Every message type either shows a modal dialog (PPC_WARNING, PPC_ERROR, PPC_INFORMATION) requiring "Press a key to continue", or writes a transient line to the minibuffer (PPC_BOTTOM_INFORMATION). Sending per-file warnings during cold start floods the user with one modal per warning, effectively locking up the editor.
15.5.3. Design Options
Option A: New protocol record type (recommended) — Add a PPC_LOG record that the Emacs client silently appends to a c-xref-log buffer. After cold start completes, send a PPC_BOTTOM_INFORMATION saying "Indexing done: N warnings (see c-xref-log)". Clean separation, no modals, inspectable at leisure. Touches protocol definition, C server code, and Emacs client.
Option B: Server-side batching — Collect all warnings during cold start into a single string, send as one PPC_INFORMATION after parsing completes. One modal instead of many. Simpler but still modal.
Option C: Summary only — Send a PPC_BOTTOM_WARNING summary to the minibuffer (e.g., "3 files could not be opened during indexing"). Details go only to the log file. Minimal change but no inspectable buffer in Emacs.
15.6. Browsing includes
15.6.1. Background
The #include preprocessor statments are referenceable items just like typenames and
variables. That means it is logical to expect that placing the cursor on an #include
line and navigation would follow the same UX as for a variable: PUSH moves cursor to the
definition (in this case the file itself) and NEXT to the next "reference", which in
this case would be the next #include statement for that file.
This does not happen.
15.6.2. Design
This needs to be investigated and understood before an attempt to design a solution can be made.
16. Major Codebase Improvements
This chapter documents internal architectural changes and technical debt reduction efforts that improve code quality, maintainability, and performance. These are improvements to c-xrefactory’s own implementation, not features users interact with directly.
For planned user-facing features, see Chapter 16: Planned Features.
16.1. Incremental cxfile.c Cleanup
16.1.1. Background
The cxfile module was designed when the disk database was the source of truth. The .cx files were not just a cache — they were the reference database. Operations like "show all references to symbol X" or "find unused symbols" were implemented as table-driven scans over the .cx file format: hash the symbol name to find the right partition, stream through it, apply a per-operation filter callback. This was efficient for the batch cross-referencer that c-xrefactory evolved from, where the workflow was c-xref -create → c-xref -update → query the on-disk database.
With the shift toward memory-as-truth (Chapter 15: Roadmap), the in-memory referenceableItemTable is becoming the authoritative source, and .cx files are becoming a startup snapshot. But cxfile.c still carries the old design: it combines disk I/O with operation-specific filtering logic, and several operations still bypass the in-memory table to read from disk directly.
16.1.2. Current Interface
The public interface (cxfile.h) reflects this mixed heritage:
// Generic persistence — correct level
extern bool loadFileNumbersFromStore(void);
extern void ensureReferencesAreLoadedFor(char *symbolName);
extern void saveReferencesToStore(bool updating, char *name);
// Operation-specific scanning — wrong level
extern void scanReferencesToCreateMenu(char *symbolName);
extern void scanForMacroUsage(char *symbolName);
extern void scanForGlobalUnused(char *cxrefFileName);
extern void scanForSearch(char *cxrefFileName);
// Implementation details leaked
extern int cxFileHashNumberForSymbol(char *symbol);
extern void searchSymbolCheckReference(ReferenceableItem *item, Reference *ref);The four scan* functions read directly from disk .cx files and merge results into the in-memory referenceableItemTable. Each encodes a specific use case (menu creation, macro completion, unused detection, symbol search) that a storage module shouldn’t know about.
The ensureReferencesAreLoadedFor function is the right pattern: load from disk into memory, then let the caller query memory. The scan* functions bypass this by combining load + filter in one step.
16.1.3. What’s Already Changing
With the memory-as-truth direction (Chapter 15), cxfile.c is already shrinking in importance:
-
loadFileNumbersFromStore()— used at startup, stays as-is -
saveReferencesToStore()— needed for snapshot writes, stays as-is -
ensureReferencesAreLoadedFor()— called 4 times (server.c, xref.c, move_function.c) to load include refs from disk db; becomes unnecessary once all include refs come from lightweight scan + full parse -
scanReferencesToCreateMenu()— called from cxref.c for browsing menus; currently reads from disk, should read from in-memory table instead -
scanForMacroUsage()— called from server.c for macro completion; same issue -
scanForGlobalUnused()— called from cxref.c; bulk scan, reasonable to keep in cxfile but should use visitor pattern -
scanForSearch()— called from cxref.c; same as above
16.1.4. Incremental Steps
These are independent improvements, not a phased plan:
Make cxFileHashNumberForSymbol static. It’s a partitioning implementation detail. Only called internally and from one external site that can be rerouted.
Make searchSymbolCheckReference static. Move the search matching logic to the caller (search.c already exists). The storage layer shouldn’t know about search string matching.
Replace scanReferencesToCreateMenu and scanForMacroUsage with in-memory queries. Both load a symbol’s references from disk and then filter them. With entry refresh populating the in-memory table, these should query referenceableItemTable directly — the data is already there. ensureReferencesAreLoadedFor can serve as the fallback if the symbol hasn’t been loaded yet.
Convert scanForGlobalUnused and scanForSearch to visitor pattern. These need to scan all symbols, not just one — a bulk operation that makes sense as a generic scanAllReferences(visitor, context) function. The visitor decides what to do with each item (check for unused, match search pattern). The operation-specific logic moves to the callers.
16.1.5. References
-
src/cxfile.h,src/cxfile.c— current implementation -
src/search.c— already exists, natural home for search matching logic -
src/cxref.c— main caller of scan functions (lines 863, 1515, 1709, 1938) -
src/server.c— callsscanForMacroUsage(line 83) andensureReferencesAreLoadedFor(lines 238, 330)
16.2. Extract Macro Expansion Module
16.2.1. Problem Statement
The yylex.c file is 2353 lines and combines multiple responsibilities:
-
Lexical analysis and token reading
-
File and buffer management
-
Preprocessor directive processing
-
Macro expansion system (~800 lines)
The macro expansion code is a substantial, cohesive subsystem that would benefit from extraction into its own module. Currently, it’s deeply embedded in yylex.c, making both lexing and macro expansion harder to understand and test in isolation.
16.2.2. Current Architecture
The macro expansion system in yylex.c comprises:
Core Responsibilities (~800 lines)
-
Macro call expansion - Main orchestration (
expandMacroCall()) -
Argument processing - Collection and recursive expansion
-
Token collation -
##operator implementation -
Stringification -
#operator implementation -
Memory management - Separate arenas for macro bodies (MBM) and arguments (PPM)
-
Cyclic detection - Preventing infinite macro recursion
Key State
int macroStackIndex; // Current macro expansion depth
static LexemStream macroInputStack[MACRO_INPUT_STACK_SIZE];
static Memory macroBodyMemory; // Long-lived: macro definitions
static Memory macroArgumentsMemory; // Short-lived: expansion temporariesMemory Lifetime Separation
The system uses two distinct memory arenas with different lifetimes:
-
MBM (Macro Body Memory): Persistent storage for macro definitions throughout compilation
-
PPM (PreProcessor Memory): Temporary storage for expansion, collation, and argument processing
This separation is fundamental and should be preserved in any refactoring.
16.2.3. Proposed Solution
Extract macro expansion into a new module: macroexpansion.c/h
Public Interface
The new module would expose a minimal, focused API:
// Initialization
void initMacroExpansion(void);
int getMacroBodyMemoryIndex(void);
void setMacroBodyMemoryIndex(int index);
// Core expansion
bool expandMacroCall(Symbol *macroSymbol, Position position);
bool insideMacro(void);
int getMacroStackDepth(void);
// Memory allocation (exposed for macro definition processing)
void *macroBodyAlloc(size_t size);
void *macroBodyRealloc(void *ptr, size_t oldSize, size_t newSize);
void *macroArgumentAlloc(size_t size);Module Boundaries
What moves to macroexpansion.c:
-
Macro call expansion and argument processing
-
Token collation (
collate()and helpers) -
Stringification (
macroArgumentsToString()) -
Cyclic call detection
-
MBM/PPM memory management
-
Buffer expansion utilities (
expandPreprocessorBufferIfOverflow(), etc.)
What remains in yylex.c:
-
Lexing and file input
-
Preprocessor directive processing (
#define,#ifdef, etc.) -
Include file handling
-
Main
yylex()function -
Macro symbol table operations
Dependencies:
The macro module would depend on:
-
Lexem stream operations (reading/writing)
-
Symbol lookup (
findMacroSymbol()) -
Cross-referencing (for collation and expansion references)
-
Current input state (via accessor functions)
16.2.4. Benefits
Architectural
-
Separation of concerns: Lexing vs. preprocessing clearly separated
-
Reduced file size: yylex.c drops from 2353 → ~1550 lines (34% reduction)
-
Testability: Macro expansion can be unit tested independently
-
Clearer ownership: Macro state and memory management centralized
Maintainability
-
Focused modules: Each file has a single, clear purpose
-
Easier reasoning: Macro behavior isolated from lexer concerns
-
Better documentation: Module-level documentation for macro system
Future flexibility
-
Could support different macro systems (C vs. C++)
-
Easier to add macro debugging/tracing
-
Independent optimization of macro expansion
16.2.5. Implementation Strategy
Phase 1: Preparation (Already Complete)
✓ Create LexemBufferDescriptor type for buffer management
✓ Refactor buffer expansion functions to use descriptor
✓ Eliminate return values for size updates
Phase 2: Create Module Structure
-
Create
macroexpansion.hwith public interface -
Create
macroexpansion.cwith initial implementations -
Move
LexemBufferDescriptorto appropriate header -
Create accessor functions for
currentInputstate
Phase 3: Incremental Function Migration
Move functions in this order (lowest risk first):
-
Memory management - MBM/PPM allocation functions
-
Buffer expansion -
expandPreprocessorBufferIfOverflow(),expandMacroBodyBufferIfOverflow() -
Support utilities -
cyclicCall(),prependMacroInput() -
Token processing -
collate(),resolveMacroArgument(), etc. -
Core expansion -
expandMacroCall(),createMacroBodyAsNewStream(), etc.
Phase 4: Integration and Cleanup
-
Update yylex.c to use new interface
-
Run full test suite after each migration step
-
Add focused unit tests for macro expansion
-
Update build system
-
Document the new architecture
16.2.6. Risks and Mitigation
Risk: Complex dependencies
Mitigation:
-
Create clear accessor functions for shared state
-
Use incremental approach - one function group at a time
-
Validate with tests after each step
Risk: Performance overhead
Mitigation:
-
Keep critical functions inline where necessary
-
Profile before/after migration
-
Current code already has abstraction layers
Assessment: Low risk - macro operations are complex enough that function call overhead is negligible
Risk: Breaking existing tests
Mitigation:
-
Run test suite after every migration step
-
Keep interface behavior identical
-
Use compiler to catch interface mismatches
16.2.7. Success Metrics
-
All existing tests pass
-
yylex.c reduced to ~1550 lines
-
New focused tests for macro expansion added
-
No performance regression (< 5% overhead acceptable)
-
Code review confirms improved clarity
16.2.8. Open Questions
-
Should
findMacroSymbol()move to the macro module or stay in yylex.c?-
It’s used by both lexer (for expansion triggering) and macro module (for nested expansions)
-
Probably belongs in a shared location or as part of symbol table operations
-
-
How to handle
currentInputglobal state?-
Options: Pass explicitly, use accessor functions, or provide context structure
-
Accessor functions likely cleanest:
getCurrentInput(),setCurrentInput()
-
-
Should we extract preprocessor directives at the same time?
-
No - keep changes focused
-
Could be a future refactoring after macro extraction proves successful
-
16.2.9. References
-
Current code:
src/yylex.clines 1327-2089 (macro expansion system) -
Memory management:
src/memory.h,src/memory.c -
Symbol operations:
src/symbol.h -
Related refactoring: [LexemStream API Improvements] addresses buffer management patterns
| This refactoring is independent of the LexemStream API improvements but would benefit from them being completed first, as they simplify buffer management patterns throughout the macro expansion code. |
16.3. Remove parseBufferUsingServer Bridge
16.3.1. Problem
Refactoring operations that need structural information from parsing (function boundaries, move target validation, parameter positions, etc.) do not call the parser directly. Instead, they go through parseBufferUsingServer() — a function that constructs magic string arguments (like "-olcxmovetarget", "-olcxgetfunctionbounds") and runs a full initServer() + callServer() cycle. This is the internal equivalent of the editor sending a command over the protocol.
// refactory.c — 7 calls like this:
parseBufferUsingServer(refactoringOptions.project, point, NULL, "-olcxpush", NULL);
parseBufferUsingServer(refactoringOptions.project, point, NULL, "-olcxsafetycheck", NULL);
parseBufferUsingServer(refactoringOptions.project, point, mark, "-olcxextract", "-olexmacro");
// parsing.c — 2 bridge calls:
parseBufferUsingServer(options.project, target, NULL, "-olcxmovetarget", NULL);
parseBufferUsingServer(options.project, marker, NULL, "-olcxgetfunctionbounds", NULL);This makes the control flow circular and hard to follow: a refactoring operation (already running inside the server) constructs fake arguments, re-enters the server, which dispatches the operation, which calls the parser, which produces a side-effect in global state, which the original caller then reads.
16.3.2. What’s Done
A clean parser API in parsing.h/c already exists and handles all call sites in server.c:
-
ParserOperationenum — type-safe operations (PARSE_TO_CREATE_REFERENCES,PARSE_TO_GET_FUNCTION_BOUNDS,PARSE_TO_VALIDATE_MOVE_TARGET,PARSE_TO_EXTRACT,PARSE_TO_TRACK_PARAMETERS,PARSE_TO_COMPLETE) -
ParsingConfigstruct — centralizes what was scattered across global flags (cursorOffset,markOffset,extractMode,targetParameterIndex, etc.) -
Operation predicates —
needsReferenceAtCursor(),allowsDuplicateReferences()replace implicit per-operation behavior -
parseToCreateReferences(fileName)— the completed pattern: direct parsing without any bridge, used by entry refresh (ADR 20) and LSP
Two convenience functions have clean APIs but still bridge internally:
-
isValidMoveTarget(target)— sets upParsingConfig, then callsparseBufferUsingServerwith"-olcxmovetarget" -
getFunctionBoundaries(marker)— sets upParsingConfig, then callsparseBufferUsingServerwith"-olcxgetfunctionbounds"
These demonstrate the migration pattern: the public API is already clean, only the implementation still bridges.
16.3.3. What Remains
9 bridge calls to eliminate (2 in parsing.c, 7 in refactory.c):
| Location | Magic string | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Validate move target position |
|
|
Find function boundaries around cursor |
|
|
Push reference for rename safety check |
|
|
Verify rename safety |
|
|
Navigate to parameter for add/delete |
|
|
Get parameter coordinates |
|
|
Extract function |
|
|
Extract macro |
|
|
Extract variable |
Each call follows the same pattern: set global flags → call parseBufferUsingServer → read results from global state. The migration for each is: set ParsingConfig fields → call parser directly → read results from the same global state.
16.3.4. Migration Pattern
The two parsing.c bridges show the pattern clearly. Today:
/* isValidMoveTarget — bridge still present */
syncParsingConfigFromOptions(options);
parsingConfig.operation = PARSE_TO_VALIDATE_MOVE_TARGET;
parsingConfig.positionOfSelectedReference = makePositionFromEditorMarker(target);
parsedInfo.moveTargetAccepted = false;
parseBufferUsingServer(options.project, target, NULL, "-olcxmovetarget", NULL);
result.valid = parsedInfo.moveTargetAccepted;The ParsingConfig is already set up — the bridge call is redundant, it just re-enters the server which re-reads the same config. Replacing it with a direct callParser() (similar to parseToCreateReferences) is the straightforward next step.
The refactory.c calls are slightly more involved because they also need buffer preloading (the editor marker’s buffer must be set as input for parsing) and some set additional global flags. But the mechanism is the same.
16.3.5. Independence
This refactoring is independent of the memory-as-truth architecture. The bridge removal is about how refactoring operations invoke parsing internally — not about where references come from or how they’re stored. It can proceed at any time, one call site at a time.
16.3.6. Code Locations
-
src/parsing.h— public API (ParserOperation, ParsingConfig, convenience functions) -
src/parsing.c— implementation, 2 remaining bridges -
src/refactory.c—parseBufferUsingServerdefinition (line 199) and 7 call sites
16.4. Remove Hashtab by Migrating to Hashlist
16.4.1. Problem Statement
The codebase has two hash table implementations generated by C macro templates:
-
hashtab (
hashtab.th/hashtab.tc): Open addressing with linear probing (HASH_SHIFT = 211). No deletion support. Overflow at ~89% fill triggers a fatal error. -
hashlist (
hashlist.th/hashlist.tc): Chaining with linked lists. Supports deletion (Delete,DeleteExact). No overflow risk.
Only two tables still use hashtab:
| Table | Module | Element Type |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
All other tables (editorBufferTable, symbolTable, referenceableItemTable) already use hashlist.
16.4.2. Why This Matters Now
The lightweight file structure scanning work (ADR 22) exposed hashtab’s limitations:
-
No deletion: We added an
isDeletedbitfield toFileItemand amarkFileAsDeleted()function as a workaround because hashtab cannot remove entries. With hashlist, actual deletion would be possible. -
Overflow risk:
fileTableis initialized with a fixed size. As projects grow or the lightweight scan discovers more files, the open-addressing table can overflow. Hashlist’s chaining has no such limit. -
FileItemalready hasnext: TheFileItemstruct already declaresstruct fileItem *next— currently ignored by hashtab but exactly what hashlist requires for chaining.
16.4.3. Proposed Change
Migrate fileTable and macroArgumentTable from hashtab to hashlist, then remove hashtab entirely.
fileTable migration:
-
Change
#include "hashtab.th"/#include "hashtab.tc"to hashlist equivalents infiletable.c -
FileItem.nextis already present — no struct change needed -
Replace
isDeletedworkaround with actualDelete()where appropriate -
The file number concept (index into array) changes semantics — hashlist doesn’t provide stable array indices. This needs careful thought: file numbers are used pervasively as compact identifiers. Options include maintaining a separate index array alongside the hash, or keeping the array and using hashlist only for lookup.
macroArgumentTable migration:
-
MacroArgumentTableElementcurrently has nonextfield — one must be added -
Simpler table with straightforward usage, lower risk
Remove hashtab:
-
Delete
hashtab.thandhashtab.tc -
One fewer template pattern to understand and maintain
16.4.4. File Number Semantics — The Key Challenge
The file table serves a dual purpose: hash lookup by name AND array indexing by file number. File numbers are used throughout the codebase as compact identifiers (stored in references, positions, sessions, etc.).
Hashtab provides both naturally — the hash slot index is the file number. Hashlist doesn’t — elements live in chains, not at stable array positions.
Possible approaches:
-
Parallel array: Keep a
FileItem *filesByNumber[]array for O(1) index lookup, use hashlist for name-based lookup. Two data structures, but each is simple. -
Sequence number on FileItem: Add an
int fileNumberfield, allocate sequentially. Hashlist for lookup, linear scan or secondary array for index access. -
Keep current array, add chaining: Use the existing array as the primary storage, but add chain pointers for collision resolution instead of open-addressing probing. Essentially a custom hybrid.
The parallel array approach is likely cleanest — it separates the two concerns (name lookup vs number lookup) explicitly.
16.4.5. Benefits
-
One hash pattern instead of two: Reduces cognitive load and maintenance surface
-
Real deletion: No more
isDeletedworkarounds — entries can be properly removed -
No overflow risk: Chaining grows naturally; no fatal error on high fill
-
Consistent codebase: All hash tables use the same pattern
16.4.6. Notes
-
The
isDeletedfield andmarkFileAsDeleted()function were added during TDD ofprojectstructure.c. They work as an interim solution but add complexity to every iteration over the file table (must checkisDeleted). -
Migration should be done after the lightweight scanning integration is complete, since it touches the same code.
16.5. Split the Editor Module
16.5.1. Problem Statement
The editor.c module (630+ lines) bundles at least four unrelated responsibilities under the misleading name "editor". The name suggests it’s about the external editor (Emacs), but most of the code has nothing to do with editor integration — it’s internal text manipulation infrastructure used by refactoring.
16.5.2. Current Responsibilities
1. Text memory allocator (editorMemory[], allocateNewEditorBufferTextSpace, freeTextSpace)
A power-of-2 block allocator for buffer text content. Custom malloc pool with free lists indexed by size class. No relationship to "editing" — this is a memory management concern.
2. In-buffer text editing (replaceStringInEditorBuffer, moveBlockInEditorBuffer, removeBlanksAtEditorMarker)
The refactoring engine’s hands — insert, delete, replace, and move text within buffers, with undo tracking and marker adjustment. This is the actual "editing" code, but it operates on the server’s internal buffers, not the external editor.
3. Reference/marker coordinate conversion (convertReferencesToEditorMarkers, convertEditorMarkersToReferences)
Bridges two coordinate systems: the reference world (file number, line, column) and the buffer world (buffer pointer, byte offset). Walks buffer text to convert line/col to offset and vice versa. Used by refactoring to go from "where are the references" to "where do I edit".
4. Content buffer lifecycle (loadFileIntoEditorBuffer, loadAllOpenedEditorBuffers, closeAllEditorBuffers, quasiSaveModifiedEditorBuffers, editorFileModificationTime)
Buffer loading, closing, quasi-save (mtime bookkeeping for refactoring), and file-stat wrappers that check buffers before falling back to filesystem. This is the content buffer management that belongs with the ContentBuffer type.
16.5.3. The Naming Problem
The "Editor" prefix pervades the codebase beyond just this module:
-
EditorMarker/EditorMarkerList— positional bookmarks into mutable buffer text -
EditorRegion— a span between two markers -
EditorUndo— undo records for text operations
None of these are about the external editor. They’re the server’s internal text manipulation primitives. TextMarker, TextRegion, TextUndo would be more accurate names, but renaming has cascading effects throughout the codebase.
16.5.4. Proposed Split
| New module | Responsibility | Current functions |
|---|---|---|
|
Power-of-2 block allocator for buffer text |
|
|
In-buffer text manipulation with undo and marker tracking |
|
|
Reference ↔ marker coordinate conversion |
|
|
Buffer lifecycle, loading, closing, quasi-save |
|
editorInit() would move to wherever initialization belongs (it currently just calls initEditorBufferTable()).
editorMapOnNonExistantFiles is a completion helper that iterates all buffers to find files existing in buffers but not on disk. It belongs with completion or content buffer management.
16.5.5. Notes
-
The split is purely mechanical — no behavior change, no renaming. Each group of functions has minimal coupling to the others.
-
The misleading "Editor" prefix on types (
EditorMarker,EditorUndo, etc.) is a separate concern. Renaming those types has large cascading effects and is not worth doing until the refactoring performance issue is resolved (currently each rename requires two full project parses viacallXref). -
editor.hcurrently re-exports headers forcontentbuffer.h,editormarker.h,undo.h— after the split, callers would include the specific headers they need.
16.6. Rename Server Operations
16.6.1. Problem Statement
Server operations use the prefix olcx (likely "on-line cross-references"), a legacy abbreviation that conveys no meaning to anyone reading the code or protocol today. Option names like -olcxpush, -olcxtagsearch, -olcxgetprojectname are opaque compared to what they could be: -push, -search, -get-project-name.
The word "tag" in search-related names (-olcxtagsearch, c-xref-search-in-tag-file, c-xref-tag-results-buffer) is a leftover from ctags and friends. There is no ctags compatibility — the term is purely misleading. The two menu entries "Search Definition in Tags" and "Search Symbol" both trigger the same OP_SEARCH operation, differing only in a filter flag (-searchdef). The word "tag" suggests they are fundamentally different, when they are not.
16.6.2. Scope
The rename touches three layers:
Protocol options (server C code + Emacs client): ~60 operations prefixed with -olcx* in options.c. These become plain descriptive names: -push, -pop, -goto, -complete, -search, -rename, -extract, -filter, -get-project-name, etc.
Emacs function and variable names: Functions like c-xref-search-in-tag-file, c-xref-get-tags, c-xref-interactive-tag-search-* and variables like c-xref-tag-results-buffer, c-xref-tag-search-mode-map.
System tests: Every commands.input file uses these option names. Mechanical update.
16.6.3. Design Decisions
Shortest clear name: Prefer -push over -browse-push. Stack operations (push, pop) are domain concepts — without understanding them you can’t understand browsing anyway. No grouping prefix needed.
Two kinds of filter: The browsing UI has two filter concepts that should remain distinct:
-
Reference filter (
-filter): narrows the reference list for the selected symbol by usage kind (all → exclude reads → definitions only) -
Menu filter (
-menu-filter): narrows the symbol menu when a name is ambiguous (all with name → exact match → exact match same file)
These could become -reference-filter and -symbol-filter for extra clarity, but -filter and -menu-filter are adequate.
No compatibility shim needed: Distribution is via git repo updates, and the Emacs upgrade menu entry kills the server, reloads elisp, and starts a new server on the next operation. Old and new never need to coexist.
16.6.4. Implementation
Support both old and new names in the option parser temporarily (two strcmp entries per option). Rename everywhere else (client, tests, docs). Remove the old names in a later commit. This eliminates any breakage window.
16.6.5. Priority
Low urgency, high value for readability. Can be done incrementally — start with the "tag" removal (search-related names only), then expand to the full olcx rename later.
17. Insights
This chapter contains notes of all insights, large and small, that I make as I work on this project. These insights should at some point be moved to some other, more structured, part of this document. But rather than trying to find a structure where each new finding fits, I’m making it easy to just dump them here. We can refactor these into a better and better structure as we go.
17.1. Yacc semantic data
As per usual a Yacc grammar requires each non-terminal to have a type.
Those types are named after which types of data they collect and
propagate. The names always starts with ast_ and then comes the
data type. For example if some non-terminal needs to propagate a
Symbol and a Position that structure would be called
ast_symbolParameterPair ("Pair" being thrown in there for good
measure…).
Each of those structures also always carries a begin and end position
for that structure. That means that any "ast" struct has three
fields, begin, end and the data. The data are sometimes a struct,
like in this case, but can also be a single value, like an int or a
pointer to a Symbol.
17.2. Navigation Architecture and Preloading
Date: 2025-12-22, updated 2026-02-21
17.2.1. How Symbol Navigation Works
Symbol navigation (PUSH/NEXT/PREVIOUS/POP) merges references from two sources:
-
Disk CXrefs Database - Reflects saved files on disk
-
In-Memory ReferenceableItem Table - Reflects current server state including preloaded editor buffers
When you PUSH on a symbol, the navigation menu creation (createSelectionMenuForOperation) does:
-
Load from disk - Scans CXrefs files for the symbol (via
scanReferencesToCreateMenu)-
Creates menu items with disk-based line numbers
-
-
Merge from memory - Maps over the in-memory table (via
putOnLineLoadedReferences)-
Adds references from parsed/preloaded buffers with current line numbers
-
Duplicate detection prevents the same reference appearing twice
-
-
Build session - Copies merged references to the navigation session
This dual-source approach allows navigation without full project parse while providing updated positions for modified files.
| Client preloading behavior and stale file detection are now documented in Chapter 8: Components under Server (Entry-Point Reparse) and Editor Extension (Preloading). |
17.2.2. Architectural Invariants
MUST be maintained:
-
Disk CXrefs = State of files on disk (from last tags generation)
-
ReferenceableItem Table = Disk state + preloaded editor buffers
-
Session references = Snapshot at PUSH time, refreshed on stale detection during NEXT/PREVIOUS
17.3. RefactoryMode Internally Calls XrefMode
Date: 2025-01-10
This section describes the refactoring architecture. The callXref() pattern described here is still used by refactoring operations. However, the server mode description below is partially outdated — the server now reparses stale preloaded files at entry and parses discovered CUs at startup (ADR-0020). See Chapter 15: Roadmap for the path toward eliminating callXref() from refactoring as well.
|
17.3.1. The Key Architectural Insight (Current Architecture)
RefactoryMode runs XrefMode as an internal sub-task to update the reference database before performing refactorings.
This is critical to understand because:
-
Refactorings need current cross-reference data to find all symbol occurrences
-
Server mode never creates/updates references (it only serves queries)
-
RefactoryMode is a separate process invocation, not part of the interactive server
17.3.2. How It Works
When a refactoring is invoked:
refactory() [refactory.c:1337]
│
├─ 1. Compute update strategy based on symbol scope/visibility
│ updateOption = computeUpdateOptionForSymbol(point)
│ • Local symbols: "" (no update - not in database)
│ • Header symbols: "-update" (full update required)
│ • Multi-file global: "-fastupdate" (incremental)
│ • Single-file global: "" (no update needed)
│
├─ 2. Perform the refactoring operation
│ renameAtPoint() / parameterManipulation() / etc.
│
└─ 3. Update references via internal XrefMode call
ensureReferencesAreUpdated(project) [line 146]
├─ Save current options
├─ Build argument vector with updateOption
├─ mainTaskEntryInitialisations(args)
└─ callXref(args, true) ← NESTS XREF MODE!17.3.3. Why Refactorings Are Separate Processes
The Emacs client spawns a separate RefactoryMode process rather than using the interactive server because:
-
Xref update can be slow - Would block the interactive server for user operations
-
Options isolation - The nested
callXref()"messes all static variables including options" (code comment, line 143-145) -
Memory requirements - Refactorings need more memory than interactive operations (see
mainTaskEntryInitialisationsallocation logic)
17.3.4. The Three Modes Relationship
ServerMode (c-xref -server)
- Loads .cx snapshot at startup, parses stale CUs
- Reparses stale preloaded files before each request (ADR 20)
- Long-running interactive process
- Handles: completion, goto-definition, push/pop navigation
XrefMode (c-xref -create / -update)
- Creates and updates .cx reference files
- Batch operation over all scheduled files
- Exits when complete
RefactoryMode (c-xref -refactory ...)
- Separate one-shot process per refactoring
- INTERNALLY calls XrefMode (via callXref) to update references
- Applies source code edits
- Exits when complete17.3.5. Code Evidence
// From refactory.c:143-145
// be very careful when calling this function as it is messing all static variables
// including options, ...
// call to this function MUST be followed by a pushing action, to refresh options
void ensureReferencesAreUpdated(char *project) {
// ...
deepCopyOptionsFromTo(&options, &savedOptions);
// Build xref arguments including update option
argumentVector[argumentCount++] = updateOption;
// Re-initialize as if starting fresh xref task
mainTaskEntryInitialisations(args);
// THE KEY CALL: Run XrefMode nested inside RefactoryMode
callXref(args, true);
// Restore options after the nested task
deepCopyOptionsFromTo(&savedOptions, &options);
}17.3.6. Implications
-
You cannot do refactorings in ServerMode - the architecture doesn’t support it
-
ServerMode never receives
-updateor-create- those are XrefMode/RefactoryMode only -
Refactorings are always consistent - they get fresh reference data before executing
-
Performance trade-off - Smart update strategies (local vs header vs multi-file) minimize update cost
-
Process isolation - Separate RefactoryMode process prevents server state corruption
17.4. The lastParsedMtime Optimization and Refactoring Conflict
Date: 2025-01-21
17.4.1. Problem Discovery
When implementing staleness detection for navigation (refreshing references when files are modified), we added an optimization to server.c:
// After parsing with preload, update lastParsedMtime
if (buffer != NULL && buffer->preLoadedFromFile != NULL) {
FileItem *fileItem = getFileItemWithFileNumber(parsingConfig.fileNumber);
fileItem->lastParsedMtime = buffer->modificationTime;
}This optimization prevents navigation from thinking a file is "stale" immediately after parsing it with preloaded content.
17.4.2. The Conflict
This broke refactoring operations (test_delete_parameter_with_preload). The problem:
-
Server parses with preload → In-memory references have correct positions (e.g., line 3)
-
lastParsedMtimeupdated → File marked as "freshly parsed" -
Refactoring triggers
callXref()→ xref checks timestamps -
xref sees
editorFileModificationTime() == lastParsedMtime→ Concludes "file already indexed" -
xref skips re-indexing → Persistent
.cxkeeps old positions (e.g., line 2) -
Refactoring uses stale
.cxdata → Wrong positions, operation fails
17.4.3. Root Cause: Two Sources of Truth
The architecture has two sources of references:
-
In-memory references (ReferenceableItemTable) - populated by parsing, used by navigation
-
Persistent .cx database - populated by xref, used by refactoring
The lastParsedMtime optimization conflated these:
* It correctly told navigation "in-memory is current"
* But incorrectly told xref "persistent database is current" (when it wasn’t)
17.4.4. The Workaround
Exclude refactoring operations from the optimization:
if (buffer != NULL && buffer->preLoadedFromFile != NULL
&& options.serverOperation != OP_RENAME
&& options.serverOperation != OP_ARGUMENT_MANIPULATION
&& options.serverOperation != OP_SAFETY_CHECK) {
fileItem->lastParsedMtime = buffer->modificationTime;
}This allows: * Navigation to use the optimization (in-memory is sufficient) * Refactoring to trigger xref re-indexing (reads preload, updates .cx correctly)
17.4.5. Architectural Lesson
This workaround highlights the fundamental tension: navigation and refactoring use different sources of truth. The proper fix is ADR-0014's unified on-demand architecture where both use the same in-memory reference database, eliminating the need for callXref() entirely.
17.4.6. Related
-
ADR-0014: Adopt On-Demand Parsing Architecture
-
Section 17.2: Unified Symbol Database Architecture
-
Section 18.3: RefactoryMode Internally Calls XrefMode (describes current architecture)
17.5. Stale File Refresh and Cross-File References
Date: 2025-01-29 (Updated: 2026-01-29)
17.5.1. Stale Detection
When navigating (PUSH/NEXT), the server detects if the current file is "stale" by comparing:
-
fileItem→lastParsedMtime(from disk database or last parse) -
buffer→modificationTime(from preloaded editor buffer)
If buffer→modificationTime > lastParsedMtime, the file is considered stale and refreshStaleReferencesInSession() is called.
17.5.2. The Refresh Algorithm
refreshStaleReferencesInSession() in cxref.c must preserve cross-file references while updating references from the modified file:
-
removeReferenceableItemsForFile()- remove old refs from in-memory table -
parseToCreateReferences()- re-parse with preload, add fresh refs to in-memory table -
Remove stale-file refs from menu - preserves cross-file refs, removes outdated positions
-
extendBrowsingMenuWithReferences()- merge fresh refs from in-memory table -
Mark file as freshly parsed (
lastParsedMtime = buffer→modificationTime) -
recomputeSelectedReferenceable()- rebuild session’s reference list from updated menu
Key insights:
-
The menu already has cross-file refs from the original PUSH operation (which scanned disk)
-
We do NOT clear menu refs and re-scan from disk during refresh
-
Scanning from disk creates problems:
addReferenceableToBrowsingMenucreates NEW menu items whenincludeFileNumberdiffers, and these new items haveselected=false -
Only SELECTED menu items contribute refs to the session’s reference list
-
So scanning would add refs to new (unselected) items, leaving the original (selected) item empty
17.5.3. Why Scanning From Disk Fails
During PUSH, createSelectionMenu creates menu items and adds them to sessionEntry→menu.
These items are marked as selected. When you NEXT, the menu’s reference list is what gets
used for navigation (via recomputeSelectedReferenceable).
If during refresh we: 1. Clear menu refs 2. Scan from disk
The scan calls createSelectionMenu which in turn calls addReferenceableToBrowsingMenu.
This function compares incoming items by (linkName, includeFileNumber, type). If the
includeFileNumber from the disk scan differs from the existing menu item’s value,
a new menu item is created with selected=false.
The refs are then added to this new unselected item, while the original selected item
has empty refs. recomputeSelectedReferenceable only processes selected items, so
navigation loses most of its references.
17.5.4. Architectural Note
This is a manifestation of the "two sources of truth" architecture. The long-term fix (per roadmap) is to parse all project files at startup, keeping complete references in memory. Then stale refresh would just re-parse the single file and the in-memory table would already have all cross-file references.
17.6. Unified In-Memory Table Discovery
Date: 2025-01-25
Investigation revealed that both XrefMode and ServerMode use the same in-memory ReferenceableItemTable. This is the key enabler for the incremental path to "Memory as Truth" (see Chapter 15: Roadmap).
handleFoundSymbolReference() in cxref.c handles references found during parsing. It calls isMemberInReferenceableItemTable() to check if a symbol exists; if not found, creates a new entry; if found, adds a reference to the existing entry. This same table is used by both modes — there is no separate "server table" vs "xref table".
The disk scan operations (ensureReferencesAreLoadedFor, scanReferencesToCreateMenu, etc.) read from .cx files on disk and also call isMemberInReferenceableItemTable() to check/merge with existing entries. If parsing has already populated the table, these operations find data already present — making them effective no-ops once all files are parsed.
18. Refactoring Recipes
This chapter documents mechanical steps for refactoring operations. Each recipe describes the algorithmic steps that an automated refactoring tool would perform.
For detailed discussions of refactoring feature architecture and implementation phases, see Chapter 16a: Planned Refactoring Features.
18.1. Existing Refactorings
Refactorings that are already implemented and available.
18.1.1. Rename Symbol
Implemented. TBD.
18.1.2. Extract Function
Implemented. TBD.
18.1.3. Reorder Parameters
Implemented. TBD.
18.1.4. Make Function Static
Purpose: Convert functions that are only used within their compilation unit to static storage class for better encapsulation and compiler optimization.
When to use:
-
Function has external linkage but no external callers
-
Want to make implementation details explicit
-
Enable compiler optimizations and reduce global namespace pollution
Input:
-
Non-static function definition
-
All references to that function
Availability:
When cursor is on a non-static function definition where all callers are in the same file.
Algorithm:
-
Check current storage class - Skip if already
static -
Find definition and all references
-
Locate function definition (not declarations)
-
Collect all call sites across project
-
-
Verify all references are local
-
For each reference (excluding definition itself):
-
Check if in same file as definition
-
If any reference is in different file, abort
-
-
Check if declared in header files (public API), abort if yes
-
-
Apply transformation
-
Find beginning of function definition
-
Insert "static " before return type
-
Output:
-
Function marked as
static -
Compiler can optimize more aggressively
-
Clear signal that function is internal
Example:
// Before - helper function with external linkage
int helperCompare(const void *a, const void *b) {
return *(int*)a - *(int*)b;
}
void publicSort(int *array, size_t n) {
qsort(array, n, sizeof(int), helperCompare);
}
// After - explicitly internal
static int helperCompare(const void *a, const void *b) {
return *(int*)a - *(int*)b;
}
void publicSort(int *array, size_t n) {
qsort(array, n, sizeof(int), helperCompare);
}Benefits:
-
Better encapsulation and code clarity
-
Enables inlining and other compiler optimizations
-
Smaller symbol tables, no name collisions
-
Safe to refactor (can’t break external code)
Notes:
-
Similar to "Unused Symbols" detection but finds LOCAL-ONLY usage instead of NO usage
-
Cannot handle functions used via function pointers passed externally (requires manual verification)
18.2. Suggested Refactorings
Refactorings that have been proposed, designed, or partially implemented but are not yet available.
18.2.1. Move Type to New File
Input:
-
Type name to move
-
Source file containing type definition
-
Target file (new or existing)
Algorithm:
-
Availability
-
Available when the selected symbol is a type, that symbol is the type to move
-
-
Identify dependencies
-
Determine what types/macros the definition references/uses
-
-
Create/update target file:
-
If new file: create with include guards and appropriate includes/forward declarations
-
If existing: open the file and find a suitable insertion location
-
-
Move definition
-
Copy type definition to target file
-
Add necessary includes and forward declarations
-
-
Replace in source file:
-
If target is new file: Replace type definition with
#include "targetfile.h" -
If target is existing file: Remove type definition, add
#include "targetfile.h"if not already present in the source file
-
Output:
-
Type definition moved to target file
-
Source file includes the target file
-
Clean compilation
Notes:
-
For new header files, steps 3-5 are particularly simple: create the new header with the type and replace the definition in source with an include
-
For existing headers, must check if include is already present before adding
-
Forward declarations (e.g.,
struct foo;) are sufficient for pointer-only dependencies -
Full type definitions or includes needed for non-pointer members
18.3. Introduce Semantic Type Aliases
Purpose: Make implicit semantic distinctions explicit by introducing type aliases for a single struct used for multiple purposes.
When to use:
-
A single struct/type is reused for semantically different purposes
-
Different usage contexts use different subsets of fields
-
Want to clarify intent without changing implementation
-
Want to prepare for future type divergence
Input:
-
Original type name (e.g.,
OlcxReferencesStack) -
List of semantic contexts where type is used (e.g., "browser", "completion", "retrieval")
-
Target file for type aliases (new or existing header)
Algorithm:
-
Analyze usage patterns - Identify distinct semantic contexts where type is used
-
Group usage sites by purpose/domain
-
Note which fields are used in each context
-
Verify that contexts are truly semantically different
-
-
Create type aliases - In appropriate header file, define semantic aliases:
c typedef OriginalType SemanticName1; typedef OriginalType SemanticName2; // etc. -
Update structure declarations - Change struct/variable declarations to use semantic types:
-
Data structure fields
-
Global variables
-
Static variables
-
-
Update function signatures - Change function parameters to use semantic types:
-
Functions operating on specific context → specific alias
-
Generic functions operating on any context → generic alias (if created)
-
-
Update call sites - Verify all usages compile with new types
-
Verify - Compile to ensure type compatibility
Output:
-
Multiple type aliases for same underlying type
-
Declarations and signatures use semantic types
-
Intent clarified through type system
-
Foundation for future divergence
Example:
Given a "kitchen sink" struct used for three purposes:
// Before - single type for everything
typedef struct OlcxReferencesStack {
OlcxReferences *top;
OlcxReferences *root;
} OlcxReferencesStack;
typedef struct SessionData {
OlcxReferencesStack browserStack; // Uses: references, symbolsMenu
OlcxReferencesStack completionsStack; // Uses: completions
OlcxReferencesStack retrieverStack; // Uses: completions
} SessionData;
void pushEmptySession(OlcxReferencesStack *stack); // GenericAfter introducing semantic aliases:
// After - semantic aliases make intent clear
typedef struct OlcxReferencesStack {
OlcxReferences *top;
OlcxReferences *root;
} OlcxReferencesStack;
// Semantic aliases
typedef OlcxReferencesStack ReferencesStack; // Generic
typedef OlcxReferencesStack BrowserStack; // For navigation
typedef OlcxReferencesStack CompletionStack; // For completion
typedef OlcxReferencesStack RetrieverStack; // For search
typedef struct SessionData {
BrowserStack browserStack;
CompletionStack completionsStack;
RetrieverStack retrieverStack;
} SessionData;
void pushEmptySession(ReferencesStack *stack); // Generic operationBenefits:
-
Intent is immediately clear from type names
-
No runtime or ABI changes (aliases compile to same type)
-
Can add domain-specific operations per type later
-
Enables gradual migration toward separate types if needed
Notes:
-
Particularly useful in C where classes/interfaces are unavailable
-
Type aliases are compile-time only - no runtime overhead
-
Can coexist with original type name during migration
-
Common pattern when refactoring legacy C code
18.3.1. Rename Included File
Purpose: Rename a file appearing in an include and update all the include directives
When to use:
-
A (header) file is inappropriately named
-
In the process of renaming a complete C "module" this is one step (until
c-xrefactorycan do all of that)
Input:
-
The old and new file names
-
All
#includelocations for the old file
Availability
When the cursor is on an #include directive. The file it references will be the "source".
Algorithm:
-
Rename the source file to the destination
-
Update all include locations
-
This will often include multiple locations
-
Output:
-
New header file
-
All
#includedirectives updated
18.3.2. Move Function to Different File
See Chapter 16a: Planned Refactoring Features for detailed design and implementation status.
Proposed refactoring to move a function definition from one C source file to another while automatically managing visibility (static vs extern) and potentially adding necessary declarations and includes.
Status: Phase 1 MVP complete.
18.3.3. Turn include guard into pragma once
Tentative.
18.3.4. Change return type
Tentative.
Purpose: Convert functions that are only used within their compilation unit to static storage class for better encapsulation and compiler optimization.
When to use:
-
Function has external linkage but no external callers
-
Want to make implementation details explicit
-
Enable compiler optimizations and reduce global namespace pollution
Input:
-
Non-static function definition
-
All references to that function
Availability:
When cursor is on a non-static function definition where all callers are in the same file.
Algorithm:
-
Check current storage class - Skip if already
static -
Find definition and all references
-
Locate function definition (not declarations)
-
Collect all call sites across project
-
-
Verify all references are local
-
For each reference (excluding definition itself):
-
Check if in same file as definition
-
If any reference is in different file, abort
-
-
Check if declared in header files (public API), abort if yes
-
-
Apply transformation
-
Find beginning of function definition
-
Insert "static " before return type
-
Output:
-
Function marked as
static -
Compiler can optimize more aggressively
-
Clear signal that function is internal
Example:
// Before - helper function with external linkage
int helperCompare(const void *a, const void *b) {
return *(int*)a - *(int*)b;
}
void publicSort(int *array, size_t n) {
qsort(array, n, sizeof(int), helperCompare);
}
// After - explicitly internal
static int helperCompare(const void *a, const void *b) {
return *(int*)a - *(int*)b;
}
void publicSort(int *array, size_t n) {
qsort(array, n, sizeof(int), helperCompare);
}Benefits:
-
Better encapsulation and code clarity
-
Enables inlining and other compiler optimizations
-
Smaller symbol tables, no name collisions
-
Safe to refactor (can’t break external code)
Notes:
-
Similar to "Unused Symbols" detection but finds LOCAL-ONLY usage instead of NO usage
-
Cannot handle functions used via function pointers passed externally (requires manual verification)
-
Estimated complexity: ~0.3× Move Function Phase 1
19. Archive
In this section you can find some descriptions and saved texts that described how things were before. They are no longer true, since that quirk, magic or bad coding is gone. But it is kept here as an archive for those wanting to do backtracking to original sources.
19.1. Memory strategies
There were a multitude of specialized memory allocation functions. In principle there where two types, static and dynamic. The dynamic could be exteded using a overflow handler.
Also one type had a struct where the actual area was extended beyond the actual struct. This was very confusing…
19.1.1. Static memory allocation
Static memory (SM_ prefix) are static areas allocated by the compiler
which is then indexed using a similarly named index variable
(e.g. ftMemory and ftMemoryIndex), something the macros took
advantage of. These are
-
ftMemory -
ppmMemory -
mbMemory
One special case of static memory also exist:
-
stackMemory- synchronous with program structure and has CodeBlock markers, so there is a specialstackMemoryInit()that initializes the outermost CodeBlock
These areas cannot be extended, when it overruns the program stops.
19.2. Trivial Prechecks
The refactorer can call the server using parseBufferUsingServer() and add some extra options (in text form).
One example is setMovingPrecheckStandardEnvironment() where it calls the server with -olcxtrivialprecheck.
However parseBufferUsingServer() uses callServer() which never answerEditAction().
In answerEditAction() the call to (unused) olTrivialRefactoringPreCheck() also requires an options.trivialPreCheckCode which is neither send by setMovingPrecheckStandardEnvironment() nor parsed by processOptions().
The only guess I have is that previously all prechecks where handled by the -olcxtrivialprecheck option in calls to the server, and have now moved to their respective refactorings.
| This theory should be checked by looking at the original source of the precheck functions and compare that with any possible checks in the corresponding refactoring code. |
19.3. Caching System
The caching system described below has been archived as it is no longer part of the current architecture.
The c-xrefactory included a sophisticated caching system that enabled incremental parsing by caching parsed input streams, parser state, and file modification tracking. This optimization allowed for faster re-analysis when only portions of source files had changed. It also allowed the system to detect out-of-memory situations, discard, flush and re-use memory during file processing.
19.3.1. Core Design Principles
Cache Point Model: The system placed strategic snapshots of parser state at external definition boundaries (functions, global variables, etc.). When files were re-processed, the system could validate cache integrity, recover from cache points, and resume parsing only from the first changed definition onward.
Separation of Concerns: Recent refactoring had separated file tracking from cache validation:
-
updateFileModificationTracking()- Updated file timestamps without side effects -
isFileModifiedSinceCached()- Pure validation function for cache integrity
19.3.2. Key Components
Cache Point Management (caching.c):
-
placeCachePoint(bool)- Placed strategic parser state snapshots -
recoverFromCache()- Restored parser state from cache points -
recoverCachePointZero()- Reset to initial cache state
File Modification Tracking:
The FileItem structure maintained multiple timestamp fields for tracking file modification:
struct FileItem {
time_t lastModified; // File's actual modification time
time_t lastInspected; // When we last checked the file
// ... other fields
}Input Stream Caching:
-
cacheInput()- Cached tokenized input from lexer -
cachingIsActive()- Checked if caching was currently enabled -
activateCaching()/deactivateCaching()- Controlled caching state
19.3.3. Parser Integration
C Parser Integration: Both C and Yacc parsers placed cache points after each external_definition, but only when not processing include files (includeStack.pointer == 0).
Parser-Specific Behavior:
-
C Parser: Full caching enabled with regular cache point placement
-
Yacc Parser: Explicitly deactivated caching via
deactivateCaching()but still placed strategic cache points -
Include Files: Cache points skipped during include processing
19.3.4. System Dependencies
The caching system was deeply integrated throughout the parsing pipeline:
| Component | Functions Used | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Lifecycle control |
|
|
Input processing |
|
|
File tracking |
|
|
File management |
|
|
Cross-reference coordination |
|
|
C grammar integration |
|
|
Yacc grammar integration |
19.3.5. Performance Characteristics
Cache Hit Scenarios:
-
Full Cache Hit: No file modifications since last parse - parser state recovered from cache point zero with minimal re-processing
-
Partial Cache Hit: File modified after Nth definition - recovery from cache point N with re-parsing only from point of change onward
-
Cache Miss: File structure changed or timestamps invalid - full re-parse with new cache points placed
Optimization Benefits:
-
Memory usage scales with number of definitions, not file size
-
File modification checking minimizes unnecessary re-reads
-
Input stream caching reduces lexer overhead
-
Strategic cache point placement enables clean recovery at definition boundaries
19.4. HUGE Memory
Previously a HUGE model was also available (by re-compilation) to reach file numbers, lines and columns above 22 bits. But if you have more than 4 million lines (or columns!) you should probably do something radical before attempting cross referencing and refactoring.
19.5. Bootstrapping
19.5.1. BOOTSTRAP REMOVED!
Once the FILL-macros was removed, we could move the enum-generation to
use the actual c-xref. So from now on we build c-xref directly
from the sources in the repo. Changes to any enums will trigger a
re-generation of the enumTxt-files but since the enumTxt-files are
only conversion of enum values to strings any mismatch will not
prevent compilation, and it would even be possible to a manual
update. This is a big improvement over the previous situation!
19.5.2. FILLs REMOVED!
As indicated in FILL macros the bootstrapping of FILL-macros has finally and fully been removed.
Gone is also the compiler_defines.h, which was just removed without
any obvious adverse effects. Maybe that will come back and bite me
when we move to more platforms other than linux and MacOS…
Left is, at this point, only the enumTxt generation, so most of the
text below is kept for historical reasons.
19.5.3. Rationale
c-xref uses a load of structures, and lists of them, that need to be created and initialized in a lot of places (such as the parsers). To make this somewhat manageable, c-xref itself parses the strucures and generates macros that can be used to fill them with one call.
c-xref is also bootstrapped into reading in a lot of predefined header files to get system definitions as "preloaded definitions".
Why this pre-loading was necessary, I don’t exactly know. It might be an optimization, or an idea that was born early and then just kept on and on. In any case it creates an extra complexity building and maintaining and to the structure of c-xref.
So this must be removed, see below.
19.5.4. Mechanism
The bootstrapping uses c-xref's own capability to parse C-code and parse those structures and spit out filling macros, and some other stuff.
This is done using options like `-task_regime_generate' which prints a lot of data structures on the standard output which is then fed into generated versions of strFill, strTdef(no longer exists) and enumTxt by the Makefile.
The process starts with building a c-xref.bs executable from checked in sources. This compile uses a BOOTSTRAP define that causes some header files to include pre-generated versions of the generated files (currently strFill.bs.h and enumTxt.bs.h) which should work in all environments.
| if you change the name of a field in a structure that is subject to FILL-generation you will need to manually update the strFill.bs.h, but a "make cleaner all" will show you where those are. |
After the c-xref.bs has been built, it is used to generate strFill and enumTxt which might include specific structures for the current environment.
HOWEVER: if FILL macros are used for structures which are different on some platforms, say a FILE structure, that FILL macro will have difference number of arguments, so I’m not sure how smart this "smart" generation technique actually is.
TODO: Investigate alternative approaches to this generate "regime", perhaps move to a "class"-oriented structure with initialization functions for each "class" instead of macros.
19.5.5. Compiler defines
In options.h there are a number of definitions which somehow are sent to the compiler/preprocessor or used so that standard settings are the same as if a program will be compiled using the standard compiler on the platform. At this point I don’t know exactly how this conversion from C declarations to compile time definitions is done, maybe just entered as symbols in one of the many symboltables?
Typical examples include "__linux" but also on some platforms things like "fpos_t=long".
I’ve implemented a mechanism that uses "gcc -E -mD" to print out and
catch all compiler defines in compiler_defines.h. This was necessary
because of such definitions on Darwin which where not in the
"pre-programmed" ones.
TODO?: As this is a more general approach it should possibly
completely replace the "programmed" ones in options.c?
19.5.6. EnumTxt generation REMOVED!
To be able to print the string values of enums the module generate.c (called when regime was RegimeGenerate) could also generate string arrays for all enums. By replacing that with some pre-processor magic for the few that was actually needed (mostly in log_trace() calls) we could do away with that whole "generate" functionality too.
(Last commit with enum generation intact is https://github.com/thoni56/c-xrefactory/commit/aafd7b1f813f2c17c684ea87ac87a0be31cdd4c4.)
19.5.7. enumTxt
For some cases the string representing the value of an Enum is needed.
c-xref handles this using the "usual" 'parse code and generate' method.
The module generate.c does this generation too.
19.5.8. Include paths
Also in options.h some standard-like include paths are added, but there is a better attempt in getAndProcessGccOptions() which uses the compiler/preprocessor itself to figure out those paths.
TODO?: This is much better and should really be the only way, I think.
19.5.9. Problems
Since at bootstrap there must exist FILL-macros with the correct field
names this strategy is an obstacle to cleaning up the code since every
field is referenced in the FILL macros. When a field (in a structure
which are filled using the FILL macro) changes name, this will make
initial compilation impossible until the names of that field is also
changed in the strFill.bs.h file.
One way to handle this is of course to use c-xrefactory itself and
rename fields. This requires that the project settings also include a
pass with BOOTSTRAP set, which it does.
19.5.10. Removing
I’ve started removing this step. In TODO.org I keep a hierarchical list of the actions to take (in a Mikado kind of style).
The basic strategy is to start with structures that no other structure
depends on. Using the script utils/struct2dot.py you can generate a
DOT graph that shows those dependencies.
Removal can be done in a couple of ways
-
If it’s a very small structure you can replace a call to a
FILL_XXX()macro with a compound literal. -
A better approach is usually to replace it with a
fillXXX()function, or even better, with anewXXX(), if it consistently is preceeded with an allocation (in the same memory!). To see what fields vary you can grep all such calls, make a CSV-file from that, and compare all rows.
19.5.11. strTdef.h
The strTdef.h was generated using the option -typedefs as a part
of the old -task_regime_generate strategy and generated typedef
declarations for all types found in the parsed files.
I also think that you could actually merge the struct definition with the typedef so that strTdef.h would not be needed. But it seems that this design is because the structures in proto.h are not a directed graph, so loops makes that impossible. Instead the typedefs are included before the structs:
#include "strTdef.h"
struct someNode {
S_someOtherNode *this;
...
struct someOtherNode {
S_someNode *that;
...
This is now ideomatically solved using the structs themselves:
struct someNode {
struct someOtherNode *this;
...
struct someOtherNode {
struct someNode *that;
...
19.6. FILL macros
The FILL macros are now fully replaced by native functions or some other, more refactoring-friendly, mechanism. Yeah!
During bootstrapping a large number of macros named __FILL_xxxx is created. The intent is that you can fill a complete structure with one call, somewhat like a constructor, but here it’s used more generally every time a complex struct needs to be initialized.
There are even _FILLF_xxx macros which allows filling fields in sub-structures at the same time.
This is, in my mind, another catastrophic hack that makes
understanding, and refactoring, c-xrefactory such a pain. Not to
mention the extra bootstrap step.
I just discovered the compound literals of C99. And I’ll experiment with replacing some of the FILL macros with compound literals assignments instead.
FILL_symbolList(memb, pdd, NULL);
could become (I think):
memb = (SymbolList){.d = pdd, .next = NULL};
If successful, it would be much better, since we could probably get rid of the bootstrap, but primarily it would be more explicit about which fields are actually necessary to set.
19.7. Users
The -user option has now been removed, both in the tool and the
editor adaptors, and with it one instance of a hashlist, the
olcxTab, which now is a single structure, the sessionData.
There is an option called -user which Emacs sets to the frame-id. To
me that indicates that the concept is that for each frame you create
you get a different "user" with the c-xref server that you (Emacs)
created.
The jedit adapter seems to do something similar:
options.add("-user");
Options.add(s.getViewParameter(data.viewId));
Looking at the sources to find when the function
olcxSetCurrentUser() is called it seems that you could have
different completion, refactorings, etc. going on at the same time in
different frames.
Completions etc. requires user interaction so they are not controlled by the editor in itself only. At first glance though, the editor (Emacs) seems to block multiple refactorings and referencs maintenance tasks running at the same time.
This leaves just a few use cases for multiple "users", and I think it adds unnecessary complexity. Going for a more "one user" approach, like the model in the language server protocol, this could really be removed.